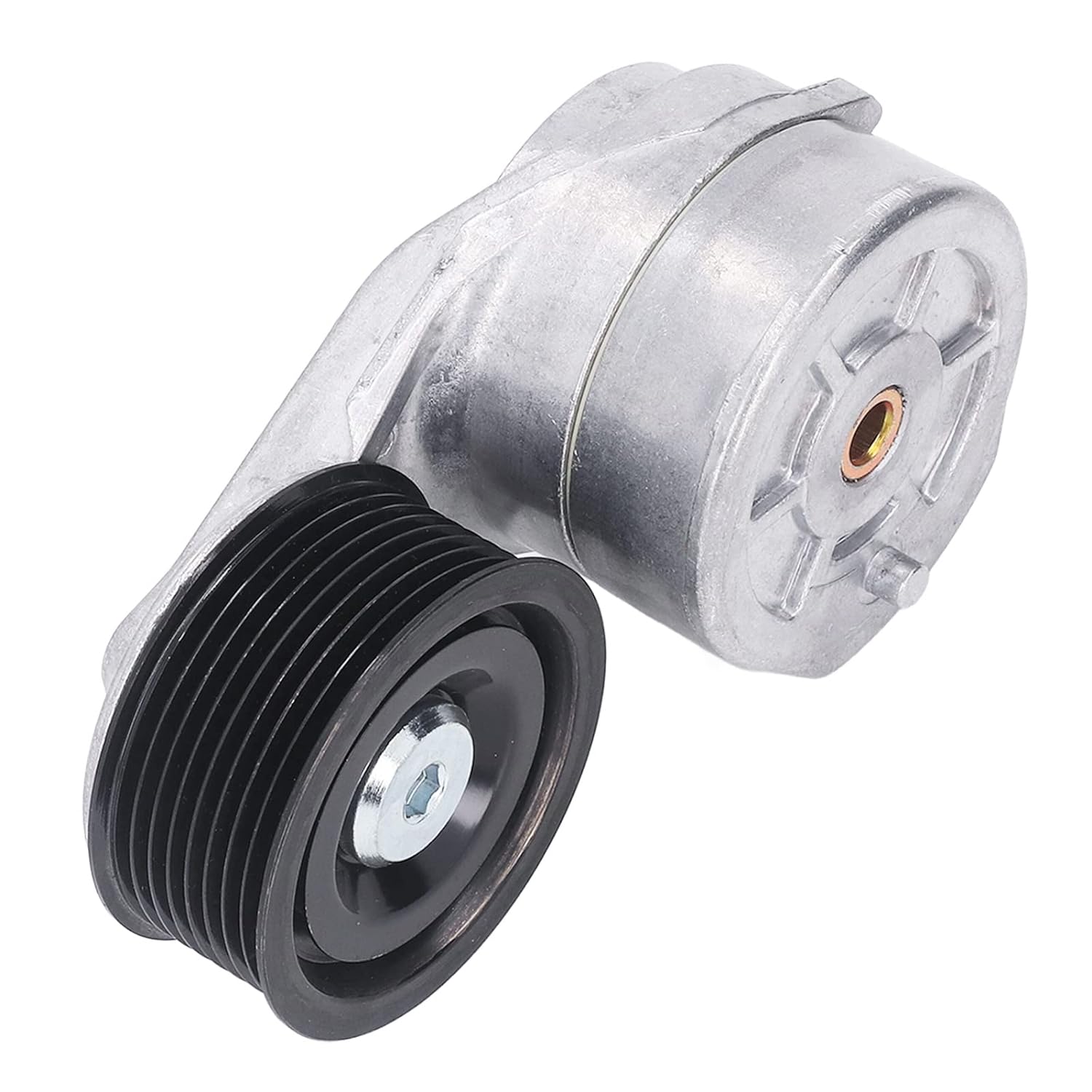
Product Description
Tensioner Pulley V-ribbed belt Car Drive Belt Tensioner for BMW / MINI
OE number:
FEBI BILSTEIN : 49526
Compatible Vehicles:
BMW 1 (F20) 2571/11-
1 (F20) 116 i
2015-
1 (F20) 118 i
2015-
1 (F20) 120 i
2016-
1 (F20) 125 i
2015-
1 (F20) M 140 i
2015-
1 (F20) M 140 i xDrive
2015-
BMW 1 (F21) 2011/12-
1 (F21) 116 i
2015-
1 (F21) 118 i
2015-
1 (F21) 120 i
2015-
1 (F21) 125 i
2015-
1 (F21) M 140 i
2015-
1 (F21) M 140 i xDrive
2015-
BMW 2 Convertible (F23) 2014/03-
2 Convertible (F23) 218 i
2015-
2 Convertible (F23) M 240 i
2015-
2 Convertible (F23) M 240 i xDrive
2015-
BMW 2 Coupe (F22, F87) 2012/10-
2 Coupe (F22, F87) 218 i
2015-
2 Coupe (F22, F87) 230 i
2015-
2 Coupe (F22, F87) M 240 i
2015-
2 Coupe (F22, F87) M 240 i xDrive
2015-
BMW 3 (F30, F80) 2011/03-
3 (F30, F80) 318 i
2015-
3 (F30, F80) 320 i
2014-
3 (F30, F80) 320 i xDrive
2014-
3 (F30, F80) 330 i
2014-
3 (F30, F80) 330 i xDrive
2014-
3 (F30, F80) 340 i
2014-
3 (F30, F80) 340 i
2014-
3 (F30, F80) 340 i xDrive
2014-
3 (F30, F80) 340 i xDrive
2017-
BMW 3 Gran Turismo (F34) 2012/07-
3 Gran Turismo (F34) 320 i
2012-2016
3 Gran Turismo (F34) 320 i xDrive
2012-2016
3 Gran Turismo (F34) 330 i
2015-
3 Gran Turismo (F34) 340 i
2015-
3 Gran Turismo (F34) 340 i xDrive
2015-
BMW 3 Touring (F31) 2011/07-
3 Touring (F31) 318 i
2015-
3 Touring (F31) 320 i
2014-
3 Touring (F31) 320 i xDrive
2014-
3 Touring (F31) 330 i
2016-
3 Touring (F31) 330 i xDrive
2014-
3 Touring (F31) 340 i
2014-
3 Touring (F31) 340 i
2014-
3 Touring (F31) 340 i xDrive
2014-
3 Touring (F31) 340 i xDrive
2014-
BMW 4 Convertible (F33, F83) 2013/10-
4 Convertible (F33, F83) 420 i
2016-
4 Convertible (F33, F83) 430 i
2016-
4 Convertible (F33, F83) 430 i xDrive
2016-
4 Convertible (F33, F83) 440 i
2016-
4 Convertible (F33, F83) 440 i
2016-
4 Convertible (F33, F83) 440 i xDrive
2016-
4 Convertible (F33, F83) 440 i xDrive
2016-
BMW 4 Coupe (F32, F82) 2013/07-
4 Coupe (F32, F82) 418 i
2016-
4 Coupe (F32, F82) 420 i
2016-
4 Coupe (F32, F82) 420 i xDrive
2016-
4 Coupe (F32, F82) 430 i
2016-
4 Coupe (F32, F82) 430 i xDrive
2016-
4 Coupe (F32, F82) 440 i
2016-
4 Coupe (F32, F82) 440 i
2016-
4 Coupe (F32, F82) 440 i xDrive
2016-
4 Coupe (F32, F82) 440 i xDrive
2016-
BMW 4 Gran Coupe (F36) 2014/03-
4 Gran Coupe (F36) 418 i
2015-
4 Gran Coupe (F36) 420 i
2016-
4 Gran Coupe (F36) 420 i xDrive
2016-
4 Gran Coupe (F36) 430 i
2016-
4 Gran Coupe (F36) 430 i xDrive
2016-
4 Gran Coupe (F36) 440 i
2016-
4 Gran Coupe (F36) 440 i
2016-
4 Gran Coupe (F36) 440 i xDrive
2016-
4 Gran Coupe (F36) 440 i xDrive
2016-
BMW 7 (G11, G12) 2014/10-
7 (G11, G12) 730 i, Li
2016-
7 (G11, G12) 740 Li
2015-
7 (G11, G12) 740 Li xDrive
2017-
MINI
COOPER 2.0L L4 Turbocharged
2571
COOPER CLUBMAN 2.0L L4 Turbocharged
2571
COOPER COUNTRYMAN 2.0L L4 Turbocharged
2571
Why choose us ?
1. Quality Control
To ensure the quality of our vehicles and other products, Our QC staffs do strict supplier evaluations, in-coming inspections, in-process inspections, final inspections and pre-delivery inspections. The most important is that we listen to what our customers say and are always looking for ways to improve the quality of our products through continuous improvement.
2. OEM Ability
We have built stable and long-term cooperate relationship with supermarkets,we can also provide ODM, OEM and Agent services to our customers over the world.
3. Parts Available
We have spare parts for immediate delivery to anywhere in the world. While our vehicles become standard with more features than anyone else, we also offer more optional parts for our vehicles than anyone else.
4. Good Warranty
We take customer satisfaction and product quality as the first priority for us. We supply reliable warranties and good after-sales services.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(",").forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Type: | Belt Tensioner |
|---|---|
| Transport Package: | Color Box Packing |
| Trademark: | VQGC, GXGK, WJT |
| Origin: | China |
| Samples: |
US$ 10/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

What is the role of belt tensioner materials and coatings in performance and longevity?
Belt tensioner materials and coatings play a crucial role in the performance and longevity of belt tensioners. The choice of materials and coatings directly impacts the tensioner's ability to withstand the forces and loads encountered in belt-driven systems, resist wear and corrosion, and maintain consistent performance over time. Here's a detailed explanation of the role of belt tensioner materials and coatings in performance and longevity:
- Strength and Durability:
- Wear Resistance:
- Corrosion Resistance:
- Friction Reduction:
- Temperature Stability:
- Lubrication Enhancement:
- Noise and Vibration Damping:
The materials used in belt tensioners need to possess high strength and durability to withstand the mechanical stresses and loads imposed on them. Tensioner components are subjected to continuous movement and contact with the belt, which can lead to wear, fatigue, and potential failure. High-strength materials, such as hardened steels or alloys, are commonly used to ensure the tensioner's structural integrity and longevity.
Belt tensioners are exposed to friction and wear as they come into contact with the belt during operation. Materials with excellent wear resistance properties, such as hardened surfaces or wear-resistant coatings, are employed to minimize the wear rate and extend the tensioner's lifespan. These materials and coatings help maintain optimal contact between the tensioner and the belt, reducing the risk of belt slippage and premature failure.
In certain environments, belt tensioners may be exposed to corrosive substances, moisture, or contaminants, which can lead to corrosion and degradation of the tensioner components. Corrosion-resistant materials, such as stainless steel or corrosion-resistant alloys, are often utilized to protect the tensioner against corrosive elements. Additionally, coatings like zinc plating or other protective finishes can be applied to enhance the tensioner's corrosion resistance.
Reducing friction between the tensioner and the belt is essential for minimizing wear and maintaining consistent tension. Materials or coatings with low friction coefficients can help reduce the frictional forces and energy losses associated with the tensioner's operation. By reducing friction, these materials and coatings contribute to improved efficiency, reduced heat generation, and increased longevity of the tensioner and the entire belt-driven system.
Belt tensioners are exposed to a wide range of operating temperatures, including both high and low extremes. Materials with good temperature stability and resistance to thermal degradation are essential for reliable tensioner performance. Heat-resistant alloys, high-temperature plastics, or thermal barrier coatings may be utilized to ensure that the tensioner maintains its mechanical properties and functionality under elevated temperatures.
Some tensioner materials or coatings are designed to enhance lubrication and reduce friction between moving parts. They may have self-lubricating properties or be compatible with specific lubricants used in the belt-driven system. These materials and coatings help reduce wear, heat generation, and the need for external lubrication, contributing to improved performance and extended longevity of the tensioner.
Belt tensioners can generate noise and vibration during operation, which can affect the comfort and performance of the belt-driven system. Certain materials or coatings can help dampen vibrations and reduce noise levels, improving the overall system's performance and minimizing potential issues associated with excessive noise or vibrations.
In summary, the choice of belt tensioner materials and coatings is critical for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Materials with high strength and durability, wear resistance, corrosion resistance, friction reduction, temperature stability, lubrication enhancement, and noise/vibration damping properties contribute to the tensioner's ability to withstand the operational demands of belt-driven systems. By selecting appropriate materials and coatings, manufacturers can enhance the reliability, durability, and overall efficiency of belt tensioners, leading to extended service life and improved performance of the belt-driven systems they are used in.

Can belt tensioners be customized or modified for unique industrial or automotive needs?
Belt tensioners can indeed be customized or modified to meet unique industrial or automotive needs. The design and functionality of belt tensioners can be adapted to specific requirements, allowing for greater versatility and compatibility in various applications. Here's a detailed explanation of how belt tensioners can be customized or modified for unique needs:
- Tensioner Design:
- Tensioner Material:
- Tensioner Force and Range:
- Tensioner Damping and Vibration Control:
- Environmental Considerations:
- Integration with Monitoring Systems:
The design of belt tensioners can be customized to accommodate different space constraints, mounting configurations, and belt drive layouts. Manufacturers can offer various tensioner designs, including compact tensioners, offset tensioners, or multi-belt tensioners, to address specific installation requirements. By adapting the tensioner design, it becomes possible to integrate the tensioner seamlessly into unique industrial or automotive systems.
Belt tensioners are typically constructed using durable materials such as cast iron, steel, or aluminum. However, for specific applications that involve extreme temperatures, corrosive environments, or weight considerations, the tensioner material can be customized. For example, in high-temperature environments, tensioners can be made from heat-resistant alloys or ceramics. Customizing the tensioner material ensures optimal performance and longevity in unique operating conditions.
The tensioning force and tension range of belt tensioners can be tailored to suit specific applications. Different industrial or automotive systems may require varying tension levels based on factors like load requirements, operating conditions, or desired power transmission efficiency. Manufacturers can customize the tensioner force and range to match these specific needs, ensuring the proper tension is maintained in the belt drive system.
Customized belt tensioners can incorporate damping and vibration control features to address specific noise and vibration requirements. In applications where noise reduction or vibration dampening is critical, tensioners can be modified with additional components or materials to absorb or dampen vibrations, resulting in smoother and quieter operation.
Specialized belt tensioners can be customized for unique environmental conditions. For instance, in applications exposed to high levels of dust, moisture, or chemicals, tensioners can be modified with protective coatings, seals, or materials that enhance resistance to corrosion, abrasion, or contamination. By customizing the tensioners to withstand harsh environments, their performance and service life can be optimized.
In some cases, belt tensioners can be modified to integrate with monitoring systems or sensors. This customization allows for real-time monitoring of belt tension and condition, enabling proactive maintenance or automated adjustments. Integration with monitoring systems provides enhanced control and efficiency, particularly in critical industrial or automotive applications.
In summary, belt tensioners can be customized or modified to meet unique industrial or automotive needs. Customization options include adapting the tensioner design, selecting appropriate materials, adjusting the tensioning force and range, incorporating damping and vibration control features, considering environmental factors, and integrating with monitoring systems. By customizing belt tensioners, they can be optimized for specific applications, ensuring reliable performance and longevity in diverse operating conditions.

Can you describe the various types of belt tensioners, such as automatic or manual tensioners?
There are various types of belt tensioners available, each designed to fulfill specific requirements in maintaining belt tension. Here's a description of the different types of belt tensioners:
- Manual Belt Tensioners:
- Automatic Belt Tensioners:
- Hydraulic Belt Tensioners:
- Eccentric Belt Tensioners:
- Idler Pulley Tensioners:
Manual belt tensioners are the most basic type and require manual adjustment to set and maintain the desired tension. They typically consist of an adjustable arm or bracket that can be moved to increase or decrease the tension in the belt. Manual tensioners are commonly used in applications where tension adjustments are infrequent or can be easily accessed for manual adjustment. They are simple, cost-effective, and widely used in various industries.
Automatic belt tensioners, also known as self-adjusting or spring-loaded tensioners, are designed to maintain the proper tension automatically. They incorporate a spring mechanism that applies constant tension to the belt, compensating for belt elongation and wear over time. Automatic tensioners are commonly used in applications where frequent manual adjustments are impractical or where consistent tension control is essential. They provide convenience, minimize maintenance requirements, and ensure optimal tension without the need for manual intervention.
Hydraulic belt tensioners utilize hydraulic pressure to maintain belt tension. They consist of a hydraulic cylinder or piston that applies force to the tensioner arm, adjusting the tension in the belt. Hydraulic tensioners are commonly used in applications with high load requirements or variable operating conditions. They provide precise tension control, can compensate for changes in temperature and load, and are often employed in heavy-duty industrial machinery and automotive applications.
Eccentric belt tensioners use an eccentric mechanism to adjust the tension in the belt. They typically feature an eccentric pulley or roller that can be rotated to increase or decrease the tension. Eccentric tensioners are commonly used in applications where precise tension adjustments are required, such as high-performance engines or systems with specific belt tension specifications. They offer fine-tuning capabilities and are often found in automotive racing, performance tuning, and specialized machinery.
Idler pulley tensioners, also known as fixed tensioners or idler pulley assemblies, are a type of belt tensioner that utilizes an idler pulley to maintain tension. They are typically positioned on the slack side of the belt, providing guidance and tension control. Idler pulley tensioners are commonly used in applications where a fixed tension is desired, and the tensioning capability is provided by other components in the system, such as an automatic tensioner or an adjustable drive pulley.
In addition to these types, there are also specialized belt tensioners designed for specific applications or industries, such as torsional vibration dampers used in automotive engines to reduce vibrations, or belt tensioners with built-in dampening mechanisms to minimize noise in certain applications.
Overall, the choice of belt tensioner depends on factors such as the application requirements, load conditions, frequency of tension adjustments, and the desired level of automation and control. Selecting the appropriate type of belt tensioner is crucial to maintaining optimal belt tension and ensuring the efficient and reliable operation of belt-driven systems.


editor by CX 2024-05-02
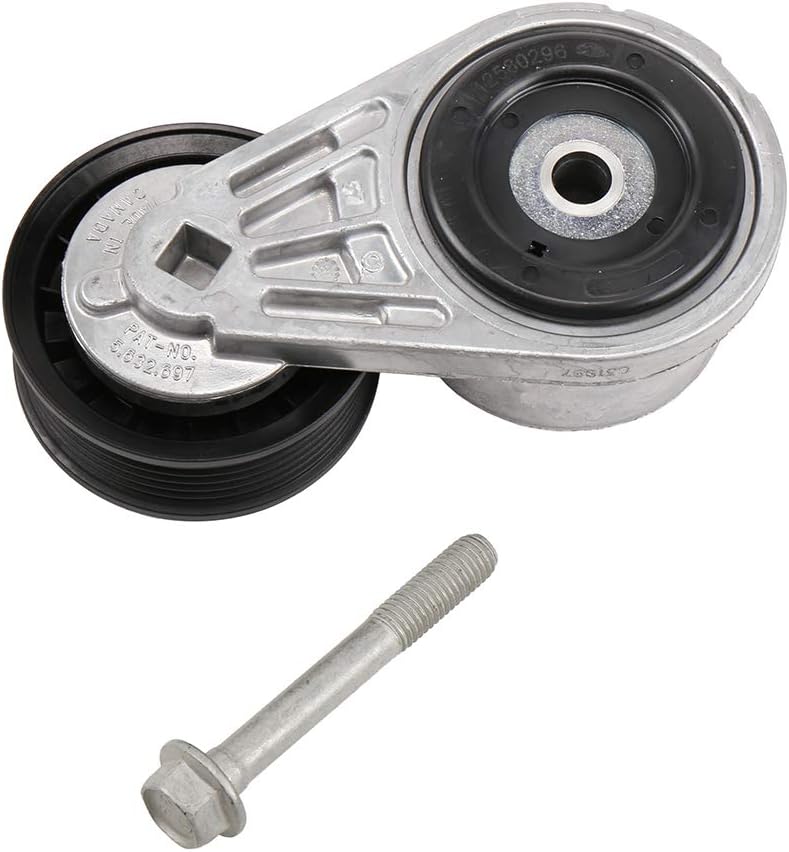
China Custom Tensioner Pulley V-Ribbed Belt Car Drive Belt Tensioner 11288570439 for BMW / Mini dexter axle
Product Description
Tensioner Pulley V-ribbed belt Car Drive Belt Tensioner for BMW / MINI
OE number:
FEBI BILSTEIN : 49526
Compatible Vehicles:
BMW 1 (F20) 2571/11-
1 (F20) 116 i
2015-
1 (F20) 118 i
2015-
1 (F20) 120 i
2016-
1 (F20) 125 i
2015-
1 (F20) M 140 i
2015-
1 (F20) M 140 i xDrive
2015-
BMW 1 (F21) 2011/12-
1 (F21) 116 i
2015-
1 (F21) 118 i
2015-
1 (F21) 120 i
2015-
1 (F21) 125 i
2015-
1 (F21) M 140 i
2015-
1 (F21) M 140 i xDrive
2015-
BMW 2 Convertible (F23) 2014/03-
2 Convertible (F23) 218 i
2015-
2 Convertible (F23) M 240 i
2015-
2 Convertible (F23) M 240 i xDrive
2015-
BMW 2 Coupe (F22, F87) 2012/10-
2 Coupe (F22, F87) 218 i
2015-
2 Coupe (F22, F87) 230 i
2015-
2 Coupe (F22, F87) M 240 i
2015-
2 Coupe (F22, F87) M 240 i xDrive
2015-
BMW 3 (F30, F80) 2011/03-
3 (F30, F80) 318 i
2015-
3 (F30, F80) 320 i
2014-
3 (F30, F80) 320 i xDrive
2014-
3 (F30, F80) 330 i
2014-
3 (F30, F80) 330 i xDrive
2014-
3 (F30, F80) 340 i
2014-
3 (F30, F80) 340 i
2014-
3 (F30, F80) 340 i xDrive
2014-
3 (F30, F80) 340 i xDrive
2017-
BMW 3 Gran Turismo (F34) 2012/07-
3 Gran Turismo (F34) 320 i
2012-2016
3 Gran Turismo (F34) 320 i xDrive
2012-2016
3 Gran Turismo (F34) 330 i
2015-
3 Gran Turismo (F34) 340 i
2015-
3 Gran Turismo (F34) 340 i xDrive
2015-
BMW 3 Touring (F31) 2011/07-
3 Touring (F31) 318 i
2015-
3 Touring (F31) 320 i
2014-
3 Touring (F31) 320 i xDrive
2014-
3 Touring (F31) 330 i
2016-
3 Touring (F31) 330 i xDrive
2014-
3 Touring (F31) 340 i
2014-
3 Touring (F31) 340 i
2014-
3 Touring (F31) 340 i xDrive
2014-
3 Touring (F31) 340 i xDrive
2014-
BMW 4 Convertible (F33, F83) 2013/10-
4 Convertible (F33, F83) 420 i
2016-
4 Convertible (F33, F83) 430 i
2016-
4 Convertible (F33, F83) 430 i xDrive
2016-
4 Convertible (F33, F83) 440 i
2016-
4 Convertible (F33, F83) 440 i
2016-
4 Convertible (F33, F83) 440 i xDrive
2016-
4 Convertible (F33, F83) 440 i xDrive
2016-
BMW 4 Coupe (F32, F82) 2013/07-
4 Coupe (F32, F82) 418 i
2016-
4 Coupe (F32, F82) 420 i
2016-
4 Coupe (F32, F82) 420 i xDrive
2016-
4 Coupe (F32, F82) 430 i
2016-
4 Coupe (F32, F82) 430 i xDrive
2016-
4 Coupe (F32, F82) 440 i
2016-
4 Coupe (F32, F82) 440 i
2016-
4 Coupe (F32, F82) 440 i xDrive
2016-
4 Coupe (F32, F82) 440 i xDrive
2016-
BMW 4 Gran Coupe (F36) 2014/03-
4 Gran Coupe (F36) 418 i
2015-
4 Gran Coupe (F36) 420 i
2016-
4 Gran Coupe (F36) 420 i xDrive
2016-
4 Gran Coupe (F36) 430 i
2016-
4 Gran Coupe (F36) 430 i xDrive
2016-
4 Gran Coupe (F36) 440 i
2016-
4 Gran Coupe (F36) 440 i
2016-
4 Gran Coupe (F36) 440 i xDrive
2016-
4 Gran Coupe (F36) 440 i xDrive
2016-
BMW 7 (G11, G12) 2014/10-
7 (G11, G12) 730 i, Li
2016-
7 (G11, G12) 740 Li
2015-
7 (G11, G12) 740 Li xDrive
2017-
MINI
COOPER 2.0L L4 Turbocharged
2571
COOPER CLUBMAN 2.0L L4 Turbocharged
2571
COOPER COUNTRYMAN 2.0L L4 Turbocharged
2571
Why choose us ?
1. Quality Control
To ensure the quality of our vehicles and other products, Our QC staffs do strict supplier evaluations, in-coming inspections, in-process inspections, final inspections and pre-delivery inspections. The most important is that we listen to what our customers say and are always looking for ways to improve the quality of our products through continuous improvement.
2. OEM Ability
We have built stable and long-term cooperate relationship with supermarkets,we can also provide ODM, OEM and Agent services to our customers over the world.
3. Parts Available
We have spare parts for immediate delivery to anywhere in the world. While our vehicles become standard with more features than anyone else, we also offer more optional parts for our vehicles than anyone else.
4. Good Warranty
We take customer satisfaction and product quality as the first priority for us. We supply reliable warranties and good after-sales services.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(",").forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Type: | Belt Tensioner |
|---|---|
| Transport Package: | Color Box Packing |
| Trademark: | VQGC, GXGK, WJT |
| Origin: | China |
| Samples: |
US$ 10/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

Can you provide guidance on the selection and sizing of belt tensioners for specific belt applications?
When selecting and sizing belt tensioners for specific belt applications, several factors need to be considered to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Here's a detailed guidance on the selection and sizing of belt tensioners:
- Belt Type and Size:
- System Requirements:
- Tensioner Type:
- Tensioner Design and Mounting:
- Tensioner Load Capacity:
- Environmental Considerations:
- Manufacturer Recommendations:
Start by identifying the type and size of the belt used in the application. Belts can vary in terms of width, length, profile (V-belt, timing belt, etc.), and construction material (rubber, polyurethane, etc.). The tensioner should be compatible with the specific belt type and size to ensure proper fit and functionality.
Consider the requirements of the belt-driven system. Evaluate factors such as the desired tension level, operating speed, load conditions, and environmental factors. The tensioner should be capable of providing the required tension force while accommodating the system's operating parameters.
Choose the appropriate tensioner type based on the application's needs. Common types include automatic tensioners, idler pulley tensioners, spring-loaded tensioners, and hydraulic tensioners. Each type has its advantages and limitations, so select the one that best suits the specific belt application.
Consider the design and mounting requirements of the tensioner. Evaluate the space availability, mounting configuration, and alignment with other components in the belt drive system. Some tensioners offer adjustable mounting positions or different design variations to accommodate various installation scenarios.
Check the load capacity of the tensioner to ensure it can handle the expected loads and forces in the belt system. Consider factors such as the belt tension, shock loads, and dynamic forces. The tensioner should have adequate load capacity to prevent premature wear or failure under normal operating conditions.
Assess the environmental conditions in which the tensioner will operate. Factors such as temperature extremes, moisture, dust, chemicals, and exposure to UV radiation can impact the tensioner's performance and durability. Choose a tensioner that is designed to withstand the specific environmental challenges of the application.
Refer to the manufacturer's guidelines and recommendations for selecting and sizing the tensioner. Manufacturers often provide technical data, specifications, and selection guides that assist in choosing the appropriate tensioner for specific belt applications. Follow their recommendations to ensure compatibility and optimal performance.
It is important to note that the selection and sizing of belt tensioners may require technical expertise and consideration of specific application requirements. If in doubt, consult with belt tensioner manufacturers or industry experts who can provide further guidance based on their knowledge and experience.
In summary, when selecting and sizing belt tensioners for specific belt applications, consider the belt type and size, system requirements, tensioner type, design and mounting, load capacity, environmental conditions, and manufacturer recommendations. By carefully evaluating these factors, you can choose a suitable tensioner that ensures proper tensioning, reliable operation, and extended belt life in the belt-driven system.

What is the impact of proper belt tensioning on the lifespan and performance of belts?
Proper belt tensioning has a significant impact on the lifespan and performance of belts. Maintaining the correct tension in belts is crucial for optimal power transmission, minimizing slippage, reducing wear, and ensuring reliable operation. Here's a detailed explanation of the impact of proper belt tensioning:
- Prevents Slippage:
- Reduces Wear and Friction:
- Ensures Optimal Power Transmission:
- Reduces Maintenance Requirements:
- Enhances Belt Lifespan:
- Improves System Reliability:
Proper belt tensioning prevents slippage between the belt and the pulleys or sheaves it is running on. When belts slip, power transmission efficiency decreases, and the belt can wear rapidly. By applying the correct tension, the belt grips the pulleys or sheaves firmly, ensuring efficient power transfer and minimizing slippage, which can lead to improved performance and energy efficiency.
When belts are improperly tensioned, excessive wear and friction can occur. Insufficient tension can cause the belt to slip and slide on the pulleys, generating heat and increasing friction between the belt and the pulley surfaces. This friction leads to premature wear of the belt and the pulleys, reducing their lifespan. On the other hand, excessive tension can put excessive stress on the belt, leading to accelerated wear and potential damage. Proper belt tensioning helps to minimize wear and friction, extending the lifespan of belts and associated components.
Correct tensioning of belts ensures optimal power transmission from the driving pulley to the driven pulley. When belts are properly tensioned, they can efficiently transfer the required power without energy losses due to slippage or excessive tension. This results in improved overall system performance, as the transmitted power is effectively utilized for driving various components or performing specific tasks.
Proper belt tensioning can help reduce maintenance requirements and associated costs. When belts are correctly tensioned, they experience less wear, require fewer adjustments, and have a lower chance of failure or premature replacement. By maintaining the appropriate tension, the need for frequent belt replacements and unplanned downtime due to belt-related issues can be significantly minimized, contributing to improved productivity and cost savings.
The lifespan of belts is directly influenced by proper tensioning. When belts are under the correct tension, they experience less stress, wear, and fatigue. This can prolong the lifespan of the belt, reducing the frequency of replacements and associated costs. Additionally, proper tensioning helps to distribute the load evenly across the belt, preventing localized wear and extending the overall durability of the belt.
Proper belt tensioning contributes to the overall reliability of belt-driven systems. By maintaining the correct tension, the risk of unexpected belt failures, slippage-related issues, and associated equipment downtime is significantly reduced. This ensures that the system operates reliably, minimizing interruptions in production or operation and enhancing overall system efficiency and performance.
In summary, proper belt tensioning plays a vital role in maximizing the lifespan and performance of belts. It prevents slippage, reduces wear and friction, ensures optimal power transmission, reduces maintenance requirements, enhances belt lifespan, and improves system reliability. By following manufacturer recommendations and using appropriate tensioning techniques, operators can optimize belt performance, minimize downtime, and achieve efficient and reliable operation of belt-driven systems.

How do belt tensioners differ from other components in maintaining belt tension?
Belt tensioners play a distinct role in maintaining belt tension compared to other components in belt drive systems. Here's a detailed explanation of how belt tensioners differ from other components:
1. Tension Adjustment:
Belt tensioners are specifically designed to provide an adjustable means of maintaining the proper tension in the belt. They are equipped with mechanisms such as springs, adjustable arms, or brackets that allow for easy tension adjustment. Other components in belt drive systems, such as pulleys or idlers, do not have this specific functionality and rely on external means, such as manual adjustment or fixed positioning, to maintain tension.
2. Active Tension Control:
Belt tensioners actively control and apply force to the belt to maintain tension. They are designed to compensate for belt elongation, thermal expansion, and other factors that can affect tension over time. By applying the appropriate tension, belt tensioners help to prevent belt slippage and maintain efficient power transmission. In contrast, other components, such as fixed pulleys or idlers, do not actively control tension and rely on the initial tension set during installation.
3. Dynamic Tension Compensation:
Belt tensioners are capable of dynamically adjusting the tension in response to changes in operating conditions. For example, in automotive applications, belt tensioners can compensate for variations in engine speed, temperature fluctuations, and belt wear. They can adapt to these changes and maintain the optimal tension level. Other components, such as fixed pulleys or idlers, do not possess this dynamic tension adjustment capability.
4. Vibration and Noise Damping:
Belt tensioners often incorporate features to dampen vibrations and reduce noise in the belt drive system. They act as shock absorbers, absorbing and dissipating vibrations, which helps to minimize belt flutter and reduce noise levels. Other components, such as fixed pulleys or idlers, do not typically have built-in vibration and noise damping properties.
5. Positioning on Slack Side:
Belt tensioners are typically positioned on the slack side of the belt, between the driving pulley and the driven pulley. This positioning allows them to apply tension to the belt where it is needed most, helping to maintain proper engagement and prevent slippage. In contrast, other components, such as fixed pulleys or idlers, are positioned on the tight side of the belt and primarily serve to guide and support the belt.
6. Component Integration:
Belt tensioners are standalone components that are specifically designed for tensioning belts. They are often integrated into the belt drive system as a separate unit, allowing for easy installation, adjustment, and replacement. Other components, such as pulleys or idlers, serve different functions in the system and may be integrated into other mechanisms or structures.
In summary, belt tensioners differ from other components in belt drive systems in their ability to provide adjustable tension control, dynamic tension compensation, vibration and noise damping capabilities, specific positioning on the slack side of the belt, and as standalone components designed solely for tensioning belts. These features make belt tensioners essential for maintaining optimal tension and ensuring the efficient and reliable operation of belt drive systems.


editor by CX 2024-04-30
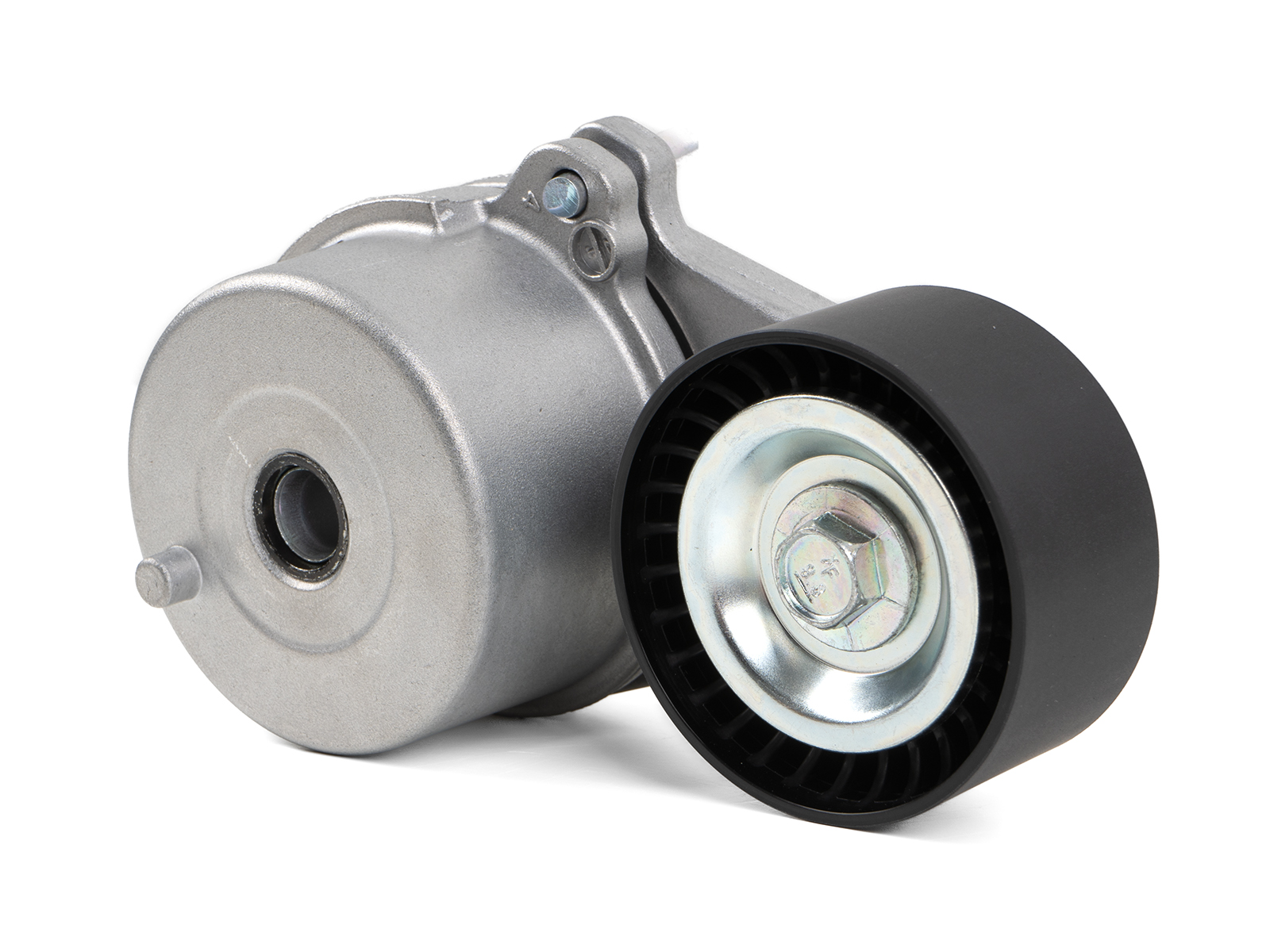
China OEM Water Pump Drive Belt Pulley Tensioner 6112340293 axle equalizer
Product Description
Water Pump Drive Belt Pulley Tensioner
| Brand | FREY |
| Market Type | Aftermarket |
| Price Term | EXW, FOB HangZhou/HangZhou |
| Payment | T/T, Paypal, West Union, L/C, Cash, etc |
| Quality | Produced according to the OE Parts |
| Delivery Time | 1-5days for stock items; 15-30days for the items need produced. |
| Shippment | DHL, Fedex,TNT,UPS, By Sea, By Air. |
| Warranty | 1 Year |
| Packing | Frey Brand, Customer Brand, Neutral Packing |
| Samples | Charge |
Specifications
1.Supply to Sounth America, Europe, Amercia, Asia
2.Certificate: ISO 9001, SGS, TUV
3.Professional Perfomance Auto parts supplier
4.Delivery Time:2-3 days if in stock; 5-15 days if out of stock
HangZhou CZPT Auto Parts Company
FREY brand was founded in 2005. Our main products focuses on serving the German car system. The products are suitable for Mercedes-Benz, BMW and other luxury car brands.
With first-class scientific research team and perfect quality control system, CZPT has covered more than 100 countries and regions in the world, adopted international advanced quality management system in quality, strict standard process control, and followed the rigorous attitude of German automotive technology. In raw material procurement, production, processing, assembly and finished products, every aspect of the process is transparent to the outside world.
Frey has always pursued the idea of internationalization. In Germany, the United Kingdom, France, Italy, Russia, Poland, Turkey, the United States and other more than 30 countries and regions, there are FREY's brand intellectual property, but also to synchronize the management system of German spare parts companies And brand requirements, bring high-quality brand experience and distinguished service experience to customers in the Chinese market.
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(",").forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Car Make: | Mercedes Benz |
|---|---|
| Car Model: | Sprinter |
| Engine Type: | Om651 M272 M273 |
| Component: | Radiator |
| Body Material: | Iron |
| Cold Style: | Water-cooled |
| Samples: |
US$ 15/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|

Can you describe the various mounting options and installations for belt tensioners in different settings?
Mounting options and installations for belt tensioners can vary depending on the specific application and the belt-driven system's design. Different settings may require different approaches to ensure proper alignment, tensioning, and functionality of the tensioner. Here's a detailed description of the various mounting options and installations for belt tensioners in different settings:
- Fixed Mounting:
- Adjustable Mounting:
- Spring-Loaded Tensioners:
- Idler Pulley Tensioners:
- Hydraulic Tensioners:
- Overhead Tensioners:
- Combination Mounting:
The most common mounting option for belt tensioners is fixed mounting. In this configuration, the tensioner is rigidly attached to a stationary part of the system, such as the engine block or a structural component. Fixed mounting provides stability and ensures that the tensioner remains in a fixed position relative to the belt. It is widely used in automotive, industrial, and machinery applications.
In some applications, adjustable mounting options are preferred to accommodate variations in belt length, alignment, or tension requirements. Adjustable tensioners allow for fine-tuning of the tensioning force by enabling adjustments in the tensioner's position. This can be achieved through slots, elongated holes, or adjustable brackets that provide flexibility in the tensioner's placement. Adjustable mounting is beneficial when precise tension adjustment is necessary or when belt drives undergo frequent changes.
Spring-loaded tensioners are commonly used in belt-driven systems. These tensioners incorporate a spring mechanism that applies constant tension to the belt. Spring-loaded tensioners can be mounted in various configurations, including fixed or adjustable mounting. The spring mechanism compensates for belt elongation, wear, or thermal expansion, ensuring consistent tension throughout the belt's operational life.
Idler pulley tensioners utilize an additional pulley to redirect the belt's path and apply tension. The tensioner is typically mounted on an adjustable bracket or arm, allowing for precise positioning of the idler pulley relative to the belt. Idler pulley tensioners are often used in serpentine belt systems, where multiple accessories are driven by a single belt. Proper alignment and tensioning of the idler pulley are crucial for efficient power transmission and belt longevity.
Hydraulic tensioners employ a hydraulic cylinder or piston to apply tension to the belt. These tensioners are commonly used in applications where high tension forces or dynamic tension control is required. Hydraulic tensioners may have specific mounting requirements due to the need for hydraulic connections, such as hoses or fittings. They are often used in heavy-duty machinery, automotive engines, or other systems demanding precise tension control.
In certain settings, such as conveyor systems or overhead power transmission systems, belt tensioners may be mounted overhead. Overhead tensioners are typically suspended from a support structure, allowing the tensioner to apply tension to the belt from above. This configuration helps maximize space utilization and facilitates maintenance and belt replacement in vertically-oriented systems.
In complex belt-driven systems, a combination of mounting options may be employed. For example, a fixed tensioner may be used in one location, while an adjustable tensioner is used in another to accommodate different belt lengths or alignment requirements. Combination mounting allows for customized tensioning solutions tailored to the specific system design and operational needs.
It is important to note that the specific mounting option and installation for a belt tensioner will depend on the system's design, space constraints, belt type, and the manufacturer's recommendations. It is essential to follow the manufacturer's guidelines and specifications for proper tensioner installation to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the belt-driven system.
In summary, the mounting options and installations for belt tensioners can include fixed mounting, adjustable mounting, spring-loaded tensioners, idler pulley tensioners, hydraulic tensioners, overhead tensioners, and combinations thereof. Each mounting option offers advantages and considerations depending on the application's requirements and the specific belt-driven system's design.

Can you provide examples of products or equipment that rely on belt tensioners for efficient operation?
Yes, there are numerous products and equipment that rely on belt tensioners for efficient operation. Belt tensioners play a crucial role in maintaining optimal tension in belts, ensuring proper power transmission, minimizing slippage, and extending the lifespan of belts and associated components. Here are some examples of products and equipment that commonly utilize belt tensioners:
- Automotive Engines:
- Industrial Machinery:
- Agricultural Equipment:
- HVAC Systems:
- Pumping Systems:
- Power Tools:
- Exercise Equipment:
Belt tensioners are essential components in automotive engines. They are commonly used in the serpentine belt system, which drives various engine accessories such as the alternator, power steering pump, air conditioning compressor, and water pump. Tensioners ensure that the serpentine belt remains properly tensioned to prevent belt slippage and maintain efficient operation of these engine accessories.
A wide range of industrial machinery relies on belt tensioners for efficient operation. Examples include conveyor systems, packaging equipment, printing machines, textile machinery, and woodworking machinery. Belt tensioners in these applications maintain proper tension in belts that drive moving components, ensuring consistent power transmission, smooth operation, and reduced downtime due to belt-related issues.
In agricultural equipment such as tractors, combines, and harvesters, belt tensioners are critical for the proper operation of belts that drive components like the fan, water pump, and various harvesting mechanisms. Tensioners help maintain optimal belt tension, preventing slippage and ensuring efficient power delivery to these vital agricultural machinery components.
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems rely on belt tensioners for efficient operation of the blower fans, compressors, and pumps. Belt tensioners in HVAC systems maintain the correct tension in belts, ensuring proper airflow, efficient cooling or heating, and reliable operation of the HVAC equipment.
Pumping systems, including water pumps, fuel pumps, and hydraulic pumps, often incorporate belt tensioners to maintain the optimal tension in belts. These tensioners contribute to efficient power transmission, preventing slippage and ensuring reliable fluid transfer in various industries, such as water treatment, oil and gas, and construction.
Belt-driven power tools, such as belt sanders, grinders, and lathes, rely on belt tensioners to maintain proper tension in the belts that drive the tool's rotating components. Tensioners in power tools ensure efficient power transfer, reduce belt wear, and enhance the tool's overall performance.
Many types of exercise equipment, including treadmills, stationary bikes, and rowing machines, incorporate belt tensioners to ensure smooth and efficient operation. These tensioners maintain proper tension in the belts that drive the equipment's resistance mechanisms, allowing users to achieve desired workout intensity and providing a consistent exercise experience.
These are just a few examples of the wide range of products and equipment that rely on belt tensioners for efficient operation. Belt tensioners are used in various industries and applications where belt-driven systems are employed, ensuring reliable power transmission, minimizing belt wear, and contributing to overall system performance and longevity.

How do belt tensioners differ from other components in maintaining belt tension?
Belt tensioners play a distinct role in maintaining belt tension compared to other components in belt drive systems. Here's a detailed explanation of how belt tensioners differ from other components:
1. Tension Adjustment:
Belt tensioners are specifically designed to provide an adjustable means of maintaining the proper tension in the belt. They are equipped with mechanisms such as springs, adjustable arms, or brackets that allow for easy tension adjustment. Other components in belt drive systems, such as pulleys or idlers, do not have this specific functionality and rely on external means, such as manual adjustment or fixed positioning, to maintain tension.
2. Active Tension Control:
Belt tensioners actively control and apply force to the belt to maintain tension. They are designed to compensate for belt elongation, thermal expansion, and other factors that can affect tension over time. By applying the appropriate tension, belt tensioners help to prevent belt slippage and maintain efficient power transmission. In contrast, other components, such as fixed pulleys or idlers, do not actively control tension and rely on the initial tension set during installation.
3. Dynamic Tension Compensation:
Belt tensioners are capable of dynamically adjusting the tension in response to changes in operating conditions. For example, in automotive applications, belt tensioners can compensate for variations in engine speed, temperature fluctuations, and belt wear. They can adapt to these changes and maintain the optimal tension level. Other components, such as fixed pulleys or idlers, do not possess this dynamic tension adjustment capability.
4. Vibration and Noise Damping:
Belt tensioners often incorporate features to dampen vibrations and reduce noise in the belt drive system. They act as shock absorbers, absorbing and dissipating vibrations, which helps to minimize belt flutter and reduce noise levels. Other components, such as fixed pulleys or idlers, do not typically have built-in vibration and noise damping properties.
5. Positioning on Slack Side:
Belt tensioners are typically positioned on the slack side of the belt, between the driving pulley and the driven pulley. This positioning allows them to apply tension to the belt where it is needed most, helping to maintain proper engagement and prevent slippage. In contrast, other components, such as fixed pulleys or idlers, are positioned on the tight side of the belt and primarily serve to guide and support the belt.
6. Component Integration:
Belt tensioners are standalone components that are specifically designed for tensioning belts. They are often integrated into the belt drive system as a separate unit, allowing for easy installation, adjustment, and replacement. Other components, such as pulleys or idlers, serve different functions in the system and may be integrated into other mechanisms or structures.
In summary, belt tensioners differ from other components in belt drive systems in their ability to provide adjustable tension control, dynamic tension compensation, vibration and noise damping capabilities, specific positioning on the slack side of the belt, and as standalone components designed solely for tensioning belts. These features make belt tensioners essential for maintaining optimal tension and ensuring the efficient and reliable operation of belt drive systems.


editor by CX 2024-02-26
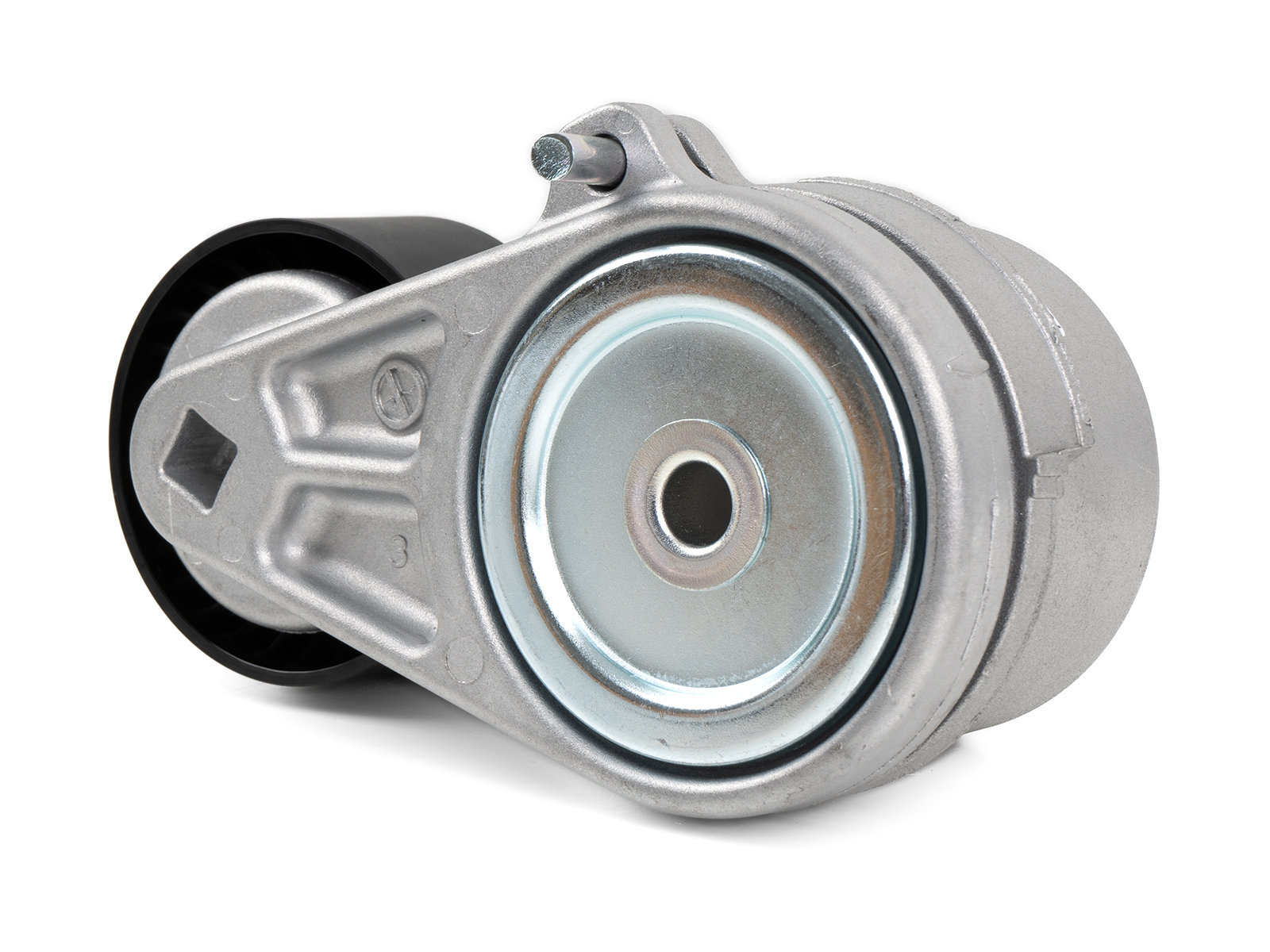
China high quality 6735884 6711698 Belt Tensioner Pulley Drive Belt Tensioner Assembly for Skid Steer Loader Toolcat 653 751 753 763 773 7753 S130 S150 S160 S175 S185 S205 S510 S5 electric rear axle kit
Product Description
Product Description
6735884 6711698 Belt Tensioner Pulley Drive Belt Tensioner Assembly for Skid Steer Loader Toolcat 773 7753 S130 S150 S160 S175 S185 S205 S510
| Part NO: | 6735884 6711698 |
| Used for: | 773 7753 S130 S150 S160 S175 S185 S205 S510 S590 |
| Related Product: | Starter/Alternator/Solenoid Valve/Overhaul Kit/Turbo Repair Kit |
| Feature: | Good quality;Fast delivery;6 Months Warranty |
Certifications
HangZhou CZPT Mechanical & Electrical Co., Ltd. is a leading provider of high-quality replacement parts for various industries. With a strong focus on customer satisfaction for over 15 years, we have established ourselves as a market leader in the following product categories:
View More Products, You Can Click Product Keywords...
| Main Products | |
| Diesel Engine Parts | Construction Equipment Parts |
| Agriculture Equipment Parts | Aerial Work Platform Parts |
| Generator Parts | |
Our comprehensive product categories include Engine parts, Electrical Parts, Hydraulic parts, Transmission parts, Classis Parts, and more. As a unique supplier, we prioritize our customers as our most valuable resource. We are dedicated to providing exceptional service and competitive prices.
OUR TEAM & EXHIBITION
Packaging & Shipping
FAQ
Q:Are you trading company or manufacturer?
A:We are trading company,but have own outsourcing factories, production quality is guaranteed.
Q:Why choose FridayParts?
A:
15+ Years Experience
176+ Countries Sold
20000+ Inventory
60000 SQ FT Warehouse
1000+ New ProductsYearly
Q: How long is your delivery time?
A: Generally it is 1-2 days if the goods are in stock. or it is 7-30 days if the goods are not in stock, it is according to quantity.
Q: Do you provide samples ? is it free or extra ?
A: Yes, we could offer the sample for quality testing but not free.
Q: How about the warranty?
A: Usually Our Warranty is 12 month. Otherwise, if any quality problem, we accept money refund in 15 days..
You can try Trade Assurance, you'll enjoy:
-- 100% product quality protection
-- 100% on-time shipment protection
-- 100% payment protection for your covered amount
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(",").forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | 12 Months |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 12 Months |
| Type: | Belt Tensioner |
| Application: | Belt Tensioner |
| Certification: | CE, ISO9001: 2000 |
| Condition: | New |
| Samples: |
US$ 641/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

Can you describe the various mounting options and installations for belt tensioners in different settings?
Mounting options and installations for belt tensioners can vary depending on the specific application and the belt-driven system's design. Different settings may require different approaches to ensure proper alignment, tensioning, and functionality of the tensioner. Here's a detailed description of the various mounting options and installations for belt tensioners in different settings:
- Fixed Mounting:
- Adjustable Mounting:
- Spring-Loaded Tensioners:
- Idler Pulley Tensioners:
- Hydraulic Tensioners:
- Overhead Tensioners:
- Combination Mounting:
The most common mounting option for belt tensioners is fixed mounting. In this configuration, the tensioner is rigidly attached to a stationary part of the system, such as the engine block or a structural component. Fixed mounting provides stability and ensures that the tensioner remains in a fixed position relative to the belt. It is widely used in automotive, industrial, and machinery applications.
In some applications, adjustable mounting options are preferred to accommodate variations in belt length, alignment, or tension requirements. Adjustable tensioners allow for fine-tuning of the tensioning force by enabling adjustments in the tensioner's position. This can be achieved through slots, elongated holes, or adjustable brackets that provide flexibility in the tensioner's placement. Adjustable mounting is beneficial when precise tension adjustment is necessary or when belt drives undergo frequent changes.
Spring-loaded tensioners are commonly used in belt-driven systems. These tensioners incorporate a spring mechanism that applies constant tension to the belt. Spring-loaded tensioners can be mounted in various configurations, including fixed or adjustable mounting. The spring mechanism compensates for belt elongation, wear, or thermal expansion, ensuring consistent tension throughout the belt's operational life.
Idler pulley tensioners utilize an additional pulley to redirect the belt's path and apply tension. The tensioner is typically mounted on an adjustable bracket or arm, allowing for precise positioning of the idler pulley relative to the belt. Idler pulley tensioners are often used in serpentine belt systems, where multiple accessories are driven by a single belt. Proper alignment and tensioning of the idler pulley are crucial for efficient power transmission and belt longevity.
Hydraulic tensioners employ a hydraulic cylinder or piston to apply tension to the belt. These tensioners are commonly used in applications where high tension forces or dynamic tension control is required. Hydraulic tensioners may have specific mounting requirements due to the need for hydraulic connections, such as hoses or fittings. They are often used in heavy-duty machinery, automotive engines, or other systems demanding precise tension control.
In certain settings, such as conveyor systems or overhead power transmission systems, belt tensioners may be mounted overhead. Overhead tensioners are typically suspended from a support structure, allowing the tensioner to apply tension to the belt from above. This configuration helps maximize space utilization and facilitates maintenance and belt replacement in vertically-oriented systems.
In complex belt-driven systems, a combination of mounting options may be employed. For example, a fixed tensioner may be used in one location, while an adjustable tensioner is used in another to accommodate different belt lengths or alignment requirements. Combination mounting allows for customized tensioning solutions tailored to the specific system design and operational needs.
It is important to note that the specific mounting option and installation for a belt tensioner will depend on the system's design, space constraints, belt type, and the manufacturer's recommendations. It is essential to follow the manufacturer's guidelines and specifications for proper tensioner installation to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the belt-driven system.
In summary, the mounting options and installations for belt tensioners can include fixed mounting, adjustable mounting, spring-loaded tensioners, idler pulley tensioners, hydraulic tensioners, overhead tensioners, and combinations thereof. Each mounting option offers advantages and considerations depending on the application's requirements and the specific belt-driven system's design.

How do belt tensioners contribute to reducing vibrations and noise in machinery?
Belt tensioners play a significant role in reducing vibrations and noise in machinery. They contribute to the smooth operation of belt-driven systems by maintaining proper belt tension, which helps minimize dynamic belt movements and associated vibrations. Here's a detailed explanation of how belt tensioners contribute to reducing vibrations and noise:
- Stabilizing Belt Movement:
- Minimizing Belt Resonance:
- Damping Vibrations:
- Reducing Belt Slippage:
- Minimizing Belt Flapping:
- Promoting Stable Rotational Motion:
Proper tensioning of belts helps stabilize their movement during operation. When belts are under the correct tension, they are less likely to experience excessive lateral or longitudinal movements. These movements, known as belt flutter or belt whip, can cause vibrations and noise. Belt tensioners apply the necessary force to keep the belt properly tensioned, preventing excessive movement and reducing the generation of vibrations and associated noise.
Belt resonance refers to the phenomenon where a belt's natural frequency coincides with the operating speed of the system, leading to excessive vibrations and noise. Proper belt tensioning helps to minimize belt resonance by ensuring that the belt operates within its stable tension range. By avoiding resonance conditions, belt tensioners contribute to a smoother operation, reducing vibrations and noise caused by belt resonance.
Belt tensioners can also act as vibration dampers. They absorb or dissipate some of the vibrations generated by the rotating components connected by the belt. The tensioner's design may incorporate features such as dampening springs or rubber elements that help absorb and dampen vibrations. This damping effect reduces the transmission of vibrations through the belt, resulting in reduced overall vibration levels and associated noise.
Improper tensioning can lead to belt slippage, where the belt slips on the pulleys or sheaves instead of maintaining a firm grip. Belt slippage generates friction and can cause vibrations and noise. Belt tensioners ensure that the belt remains properly tensioned, minimizing the risk of slippage and reducing associated vibrations and noise.
When belts are not properly tensioned, they can exhibit flapping or flailing movements, especially at higher speeds. These movements can generate vibrations and noise. Belt tensioners help maintain the correct tension, keeping the belt taut and preventing excessive flapping. By minimizing belt flapping, tensioners contribute to a smoother operation with reduced vibrations and noise.
A properly tensioned belt ensures stable rotational motion of the pulleys or sheaves it is driving. When belts are under the correct tension, they maintain a consistent grip on the pulleys, preventing sudden slips or variations in rotational motion. This stability in rotational motion helps minimize vibrations and associated noise, resulting in smoother and quieter machinery operation.
In summary, belt tensioners contribute to reducing vibrations and noise in machinery by stabilizing belt movement, minimizing belt resonance, damping vibrations, reducing belt slippage, minimizing belt flapping, and promoting stable rotational motion. By maintaining proper belt tension, tensioners help achieve smoother operation, reduce vibrations, and minimize the generation and transmission of noise, resulting in improved comfort, efficiency, and reliability of the machinery.

What industries and machinery commonly use belt tensioners for optimal belt performance?
Various industries and machinery rely on belt tensioners to achieve optimal belt performance. Here's a detailed explanation of the industries and machinery that commonly use belt tensioners:
- Automotive Industry:
- Industrial Machinery:
- Power Generation:
- Agricultural Equipment:
- Construction and Mining:
- HVAC and Refrigeration:
The automotive industry extensively utilizes belt tensioners in vehicles for various applications. Belt tensioners are commonly found in the engine accessory drive system, where they maintain the proper tension in the serpentine or V-belts that power components such as the alternator, air conditioning compressor, power steering pump, and water pump. Belt tensioners ensure efficient power transmission, reduce belt slippage, and contribute to the overall reliability and performance of automotive engines.
A wide range of industrial machinery relies on belt tensioners for optimal belt performance. Industries such as manufacturing, food processing, packaging, printing, and material handling use belt-driven systems for conveyor belts, production lines, pumps, compressors, and other equipment. Belt tensioners help maintain the proper tension in these applications, ensuring smooth operation, efficient power transmission, and minimizing downtime due to belt slippage or failure.
In the power generation sector, belt tensioners are commonly used in applications such as generators, turbines, and auxiliary equipment. These systems often utilize belts to transfer power between components, and the tensioners play a crucial role in maintaining proper belt tension. Belt tensioners help optimize power transmission efficiency, reduce vibrations, and enhance the overall reliability of the power generation equipment.
Agricultural machinery, including tractors, combines, and other farming equipment, often rely on belt-driven systems for various operations. Belt tensioners are utilized to maintain the tension in belts powering agricultural implements, such as harvesters, balers, and grain conveyors. By ensuring optimal tension, belt tensioners contribute to the efficient operation of agricultural equipment, improving productivity and reducing maintenance requirements.
Construction and mining industries commonly employ belt-driven systems in equipment such as excavators, loaders, crushers, and conveyor systems. Belt tensioners are used to maintain the proper tension in belts powering these machines, ensuring reliable and efficient operation in demanding environments. Belt tensioners help prevent belt slippage, reduce downtime, and contribute to the longevity of the equipment.
The HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) and refrigeration industries rely on belt-driven systems for various applications, including fans, blowers, compressors, and pumps. Belt tensioners are critical in maintaining the proper tension in these systems, ensuring efficient power transmission and reducing belt-related issues such as slippage or premature wear. Belt tensioners contribute to the overall performance and reliability of HVAC and refrigeration equipment.
In addition to the industries mentioned above, belt tensioners are also utilized in a wide range of other machinery and equipment, including woodworking machinery, textile machinery, marine propulsion systems, and more. The versatility and benefits of belt tensioners make them a valuable component for achieving optimal belt performance in numerous industrial and mechanical applications.


editor by CX 2024-01-23
China Hot selling Factory Auto Parts Engine Belt Tensioner for CZPT A3 A5 Drive Belt Wheel Idler Pulley Roller Assembly 481h1007071 axle boot
Product Description
Product data
|
Product Name |
Factory Auto Parts Engine Belt Tensioner for Chery A3 A5 Drive Belt Wheel Idler Pulley Roller Assembly |
|
Car Model |
for Chery A3 A5 |
|
OEM NO. |
481H1007071 |
|
Material |
Metal + Plastic |
|
Weight |
OEM Standard |
|
Size |
OEM Standard |
|
MOQ |
1 piece if we have them in stock, 50 pieces for production. |
|
Warranty |
12 Months |
|
Delivery Time |
7-25 Days |
|
Package |
Neutral, Perfectrail or Customized Packing is acceptable Neutral packing. Neutral box and brown cartons. Pallet is also available. |
|
Our Advantage |
1. The same size as original one. 2. Lower MOQ is acceptable with more models. |
Company Profile
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(",").forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | 1 Year |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 1 Year |
| Type: | Bev |
| Samples: |
US$ 2.5/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

Are there specific considerations for choosing belt tensioners in applications with varying loads or environmental conditions?
When selecting belt tensioners for applications with varying loads or environmental conditions, there are several specific considerations to keep in mind. The performance and longevity of belt tensioners can be influenced by the dynamic nature of the loads and the environmental factors they are exposed to. Here's a detailed explanation of the considerations for choosing belt tensioners in such applications:
- Load Capacity:
- Adjustability:
- Temperature Range:
- Corrosion Resistance:
- Contamination Protection:
- Shock and Vibration Resistance:
- Maintenance and Serviceability:
In applications with varying loads, it is crucial to select belt tensioners with an appropriate load capacity. The tensioner should be capable of exerting sufficient force to maintain the desired tension in the belt, even under the highest anticipated load conditions. It is important to consider the maximum peak loads, as well as any transient or shock loads that may occur during operation. Choosing a tensioner with an adequate load capacity ensures reliable and consistent tensioning performance, preventing issues like belt slippage or excessive wear.
In applications where the loads vary significantly, having an adjustable belt tensioner can be beneficial. An adjustable tensioner allows for fine-tuning of the tensioning force to accommodate different load conditions. By adjusting the tensioner's position or tension setting, the tension can be optimized for various load levels, ensuring proper belt engagement and tension throughout the operating range. This flexibility helps maintain optimal performance and reduces the risk of belt-related problems.
Environmental conditions, particularly temperature variations, can affect the performance and durability of belt tensioners. In applications with extreme temperature ranges, it is important to choose tensioners that can withstand the anticipated temperatures without compromising their functionality. High-temperature or low-temperature resistant materials and lubricants may be required to ensure that the tensioner operates reliably and maintains its mechanical properties within the specified temperature range.
Applications exposed to harsh environments, such as those with high humidity, chemicals, or saltwater, require belt tensioners with excellent corrosion resistance. Corrosion-resistant materials, such as stainless steel or specialized coatings, should be considered to protect the tensioner from corrosion and degradation. This helps maintain the tensioner's performance and extends its service life, even in challenging environmental conditions.
In environments where the belt tensioner may be exposed to contaminants like dust, dirt, or debris, it is important to choose tensioners with effective contamination protection features. Seals, shields, or covers can be incorporated into the tensioner design to prevent the ingress of contaminants that could compromise the tensioner's functionality or cause premature wear. Proper contamination protection helps ensure reliable performance and reduces the need for frequent maintenance or replacement.
Applications with significant shock or vibration levels require belt tensioners that can withstand these dynamic forces. Tensioners with robust construction, reinforced components, or dampening features can help absorb shocks and vibrations, reducing the risk of tensioner failure or damage. It is important to consider the expected shock and vibration levels in the application and select tensioners designed to handle such conditions.
Applications with varying loads or challenging environmental conditions may require more frequent inspection and maintenance of the belt tensioners. When choosing tensioners, consider factors such as accessibility for inspection, ease of adjustment or replacement, and the availability of spare parts. Tensioners that are designed for easy maintenance and serviceability can help minimize downtime and ensure the continued performance of the belt-driven system.
In summary, choosing the right belt tensioners for applications with varying loads or environmental conditions requires considering factors such as load capacity, adjustability, temperature range, corrosion resistance, contamination protection, shock and vibration resistance, and maintenance/serviceability. By carefully evaluating these considerations and selecting tensioners that meet the specific requirements of the application, optimal performance, and longevity of the belt-driven system can be ensured.

How do belt tensioners contribute to reducing vibrations and noise in machinery?
Belt tensioners play a significant role in reducing vibrations and noise in machinery. They contribute to the smooth operation of belt-driven systems by maintaining proper belt tension, which helps minimize dynamic belt movements and associated vibrations. Here's a detailed explanation of how belt tensioners contribute to reducing vibrations and noise:
- Stabilizing Belt Movement:
- Minimizing Belt Resonance:
- Damping Vibrations:
- Reducing Belt Slippage:
- Minimizing Belt Flapping:
- Promoting Stable Rotational Motion:
Proper tensioning of belts helps stabilize their movement during operation. When belts are under the correct tension, they are less likely to experience excessive lateral or longitudinal movements. These movements, known as belt flutter or belt whip, can cause vibrations and noise. Belt tensioners apply the necessary force to keep the belt properly tensioned, preventing excessive movement and reducing the generation of vibrations and associated noise.
Belt resonance refers to the phenomenon where a belt's natural frequency coincides with the operating speed of the system, leading to excessive vibrations and noise. Proper belt tensioning helps to minimize belt resonance by ensuring that the belt operates within its stable tension range. By avoiding resonance conditions, belt tensioners contribute to a smoother operation, reducing vibrations and noise caused by belt resonance.
Belt tensioners can also act as vibration dampers. They absorb or dissipate some of the vibrations generated by the rotating components connected by the belt. The tensioner's design may incorporate features such as dampening springs or rubber elements that help absorb and dampen vibrations. This damping effect reduces the transmission of vibrations through the belt, resulting in reduced overall vibration levels and associated noise.
Improper tensioning can lead to belt slippage, where the belt slips on the pulleys or sheaves instead of maintaining a firm grip. Belt slippage generates friction and can cause vibrations and noise. Belt tensioners ensure that the belt remains properly tensioned, minimizing the risk of slippage and reducing associated vibrations and noise.
When belts are not properly tensioned, they can exhibit flapping or flailing movements, especially at higher speeds. These movements can generate vibrations and noise. Belt tensioners help maintain the correct tension, keeping the belt taut and preventing excessive flapping. By minimizing belt flapping, tensioners contribute to a smoother operation with reduced vibrations and noise.
A properly tensioned belt ensures stable rotational motion of the pulleys or sheaves it is driving. When belts are under the correct tension, they maintain a consistent grip on the pulleys, preventing sudden slips or variations in rotational motion. This stability in rotational motion helps minimize vibrations and associated noise, resulting in smoother and quieter machinery operation.
In summary, belt tensioners contribute to reducing vibrations and noise in machinery by stabilizing belt movement, minimizing belt resonance, damping vibrations, reducing belt slippage, minimizing belt flapping, and promoting stable rotational motion. By maintaining proper belt tension, tensioners help achieve smoother operation, reduce vibrations, and minimize the generation and transmission of noise, resulting in improved comfort, efficiency, and reliability of the machinery.

Are there specific belt tensioner designs for different applications, like automotive or industrial equipment?
Yes, there are specific belt tensioner designs tailored for different applications, including automotive and industrial equipment. Manufacturers develop specialized belt tensioners to meet the unique requirements and operating conditions of various industries. Here's a detailed explanation of specific belt tensioner designs for different applications:
- Automotive Belt Tensioners:
- Industrial Belt Tensioners:
- Agricultural Belt Tensioners:
- HVAC and Refrigeration Belt Tensioners:
- Specialized Belt Tensioners:
Belt tensioners used in automotive applications are designed with features that address the specific needs of the automotive industry. They are typically compact, lightweight, and engineered to withstand the demanding conditions found in vehicle engines. Automotive belt tensioners often incorporate automatic tensioning mechanisms, such as spring-loaded or hydraulic designs, to provide continuous tension control and compensate for belt elongation and wear over time. They also incorporate features like torsional vibration dampers to minimize vibrations and noise. Additionally, automotive belt tensioners undergo rigorous testing to meet industry standards and ensure reliable performance in diverse driving conditions.
Industrial belt tensioners are designed to meet the requirements of heavy-duty applications in various industries, such as manufacturing, material handling, mining, and construction. These tensioners are built to withstand high loads, harsh environments, and extended operating hours. Industrial belt tensioners often feature robust construction using durable materials like cast iron or steel. They may incorporate automatic tensioning mechanisms, hydraulic systems, or eccentric designs to provide precise tension control and adaptability to changing operating conditions. Industrial belt tensioners also come in a range of sizes and configurations to accommodate different belt sizes and drive systems used in industrial machinery.
Agricultural equipment, such as tractors, combines, and harvesters, have specific belt tensioner designs suited for the demanding conditions encountered in farming operations. Agricultural belt tensioners are designed to withstand dust, debris, and exposure to outdoor elements. They often incorporate automatic tensioning mechanisms with robust spring-loaded systems to compensate for belt wear and maintain optimal tension during extended periods of use. These tensioners are engineered to provide reliable performance in agricultural machinery, contributing to efficient power transmission and reduced maintenance requirements.
Belt tensioners used in HVAC and refrigeration systems are designed to ensure reliable and efficient operation of fans, blowers, compressors, and pumps. These tensioners are typically compact and incorporate automatic tensioning mechanisms to maintain consistent belt tension under varying operating conditions. They may also include features like vibration dampening to reduce noise and enhance system performance. HVAC and refrigeration belt tensioners are engineered to meet the specific requirements of cooling and ventilation systems, contributing to energy efficiency and prolonged equipment lifespan.
There are also specialized belt tensioners designed for specific applications or industries. For example, in the woodworking industry, belt tensioners with quick-release mechanisms are used to facilitate efficient belt changes. In the textile industry, belt tensioners with precise tension control are employed to ensure proper synchronization of moving parts. Marine propulsion systems utilize belt tensioners designed for marine environments, resistant to corrosion and capable of withstanding vibration and shock. These specialized tensioners are tailored to the specific needs of their respective industries, incorporating features and materials that optimize performance and durability.
Overall, the design of belt tensioners is influenced by the unique requirements of different applications and industries. By considering factors such as load capacity, environmental conditions, tension control mechanisms, and specific industry standards, manufacturers develop belt tensioners that are well-suited for their intended applications, ensuring optimal belt performance and system reliability.


editor by CX 2024-01-12
China Professional Customized Conveyor Belt Drum Rubber Lagging Drive Pulley pulley puller
Product Description
|
|
Color |
Polymer |
Density |
Tensile strength |
Hardness |
|
Fire resistant |
black |
NR/BR |
1.35 |
15MPA |
Shore A 65±5 |
|
Normal |
black |
NR/BR |
1.32 |
8MPA |
Shore A 65±5 |
IF NEED OTHER HARDNESS, CAN BE CUSTOMIZED!
|
PRODUCT SIZE |
||
|
THICKNESS |
WIDTH |
LENGTH |
|
8mm |
1000/1200/1450/1650/1850/2000mm |
10m |
|
10mm |
1000/1200/1450/1650/1850/2000mm |
10m |
|
12mm |
1000/1200/1450/1650/1850/2000mm |
10m |
|
15mm |
1000/1200/1450/1650/1850/2000mm |
10m |
|
20mm |
1000/1200/1450/1650/1850/2000mm |
10m |
|
25mm |
1000/1200/1450/1650/1850/2000mm |
10m |
|
30mm |
1000/1200/1450/1650/1850/2000mm |
10m |
| Material: | Natural Rubber |
|---|---|
| Usage: | Pulley Lagging |
| Feature: | Wear-resistant, Corrosion-resistant |
| Raw Materials: | Natural Rubber, Pad |
| Medium: | Pure Gum Rubber Sheet and Fabric |
| Performance: | Stripe Antiskid Rubber Sheet |
| Samples: |
US$ 10/Square Meter
1 Square Meter(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

How to use the pulley system
Using a pulley system is a great way to move things around your home, but how do you use a pulley system? Let's look at the basic equations that describe a pulley system, the types of pulleys, and some safety considerations when using pulleys. Here are some examples. Don't worry, you'll find all the information you need in one place!
Basic equations of pulley systems
The pulley system consists of pulleys and chords. When the weight of the load is pulled through the rope, it slides through the groove and ends up on the other side. When the weight moves, the applied force must travel nx distance. The distance is in meters. If there are four pulleys, the distance the rope will travel will be 2x24. If there are n pulleys, the distance traveled by the weight will be 2n - 1.
The mechanical advantage of the pulley system increases with distance. The greater the distance over which the force is applied, the greater the leverage of the system. For example, if a set of pulleys is used to lift the load, one should be attached to the load and the other to the stand. The load itself does not move. Therefore, the distance between the blocks must be shortened, and the length of the line circulating between the pulleys must be shortened.
Another way to think about the acceleration of a pulley system is to think of ropes and ropes as massless and frictionless. Assuming the rope and pulley are massless, they should have the same magnitude and direction of motion. However, in this case the quality of the string is a variable that is not overdone. Therefore, the tension vector on the block is labeled with the same variable name as the pulley.
The calculation of the pulley system is relatively simple. Five mechanical advantages of the pulley system can be found. This is because the number of ropes supporting the load is equal to the force exerted on the ropes. When the ropes all move in the same direction, they have two mechanical advantages. Alternatively, you can use a combination of movable and fixed pulleys to reduce the force.
When calculating forces in a pulley system, you can use Newton's laws of motion. Newton's second law deals with acceleration and force. The fourth law tells us that tension and gravity are in equilibrium. This is useful if you need to lift heavy objects. The laws of motion help with calculations and can help you better understand pulley systems.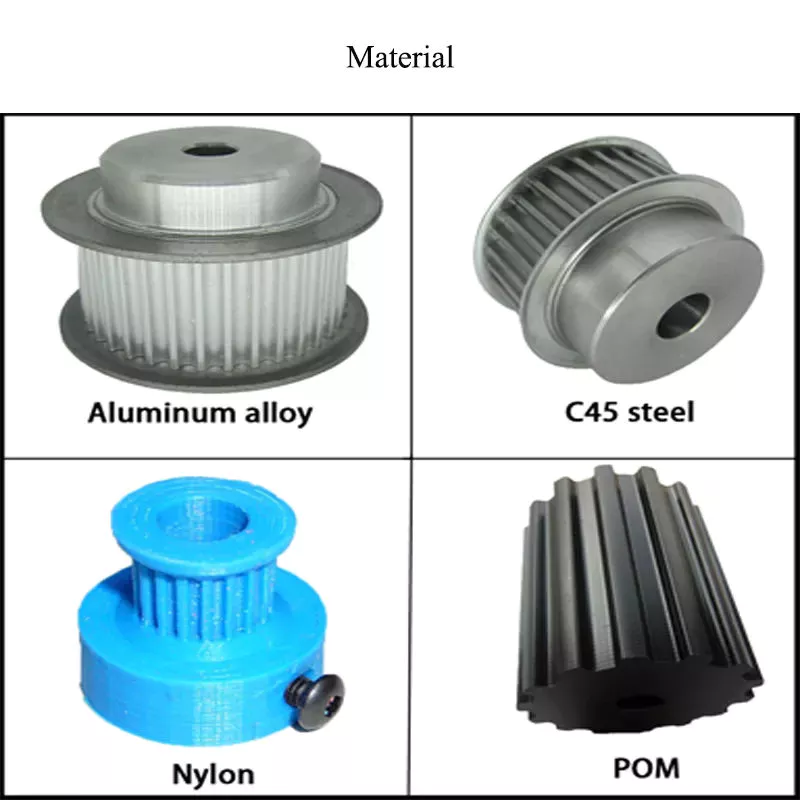
Types of pulleys
Different types of pulleys are commonly used for various purposes, including lifting. Some pulleys are flexible, which means they can move freely around a central axis and can change the direction of force. Some are fixed, such as hinges, and are usually used for heavier loads. Others are movable, such as coiled ropes. Whatever the purpose, pulleys are very useful in raising and lowering objects.
Pulleys are common in many different applications, from elevators and cargo lift systems to lights and curtains. They are also used in sewing machine motors and sliding doors. Garage and patio doors are often equipped with pulleys. Rock climbers use a pulley system to climb rocks safely. These pulley systems have different types of pinions that allow them to balance weight and force direction.
The most common type of pulley is the pulley pulley system. The pulley system utilizes mechanical advantages to lift weight. Archimedes is thought to have discovered the pulley around 250 BC. in ancient Sicily. Mesopotamians also used pulleys, they used ropes to lift water and windmills. Pulley systems can even be found at Stonehenge.
Another type of pulley is called a compound pulley. It consists of a set of parallel pulleys that increase the force required to move large objects. This type is most commonly used in rock climbing and sailing, while composite pulleys can also be found in theater curtains. If you're wondering the difference between these two types of pulleys, here's a quick overview:
Mechanical Advantages of Pulley Systems
Pulley systems offer significant mechanical advantages. The ability of the system to reduce the effort required to lift weights increases with the number of rope loops. This advantage is proportional to the number of loops in the system. If the rope had only one loop, then a single weight would require the same amount of force to pull. But by adding extra cycles, the force required will be reduced.
The pulley system has the advantage of changing the direction of the force. This makes it easier to move heavy objects. They come in both fixed and mobile. Pulleys are used in many engineering applications because they can be combined with other mechanisms. If you want to know what a pulley can do, read on! Here are some examples. Therefore, you will understand how they are used in engineering.
Single-acting pulleys do not change direction, but compound pulleys do. Their mechanical advantage is six. The compound pulley system consists of a movable pulley and a fixed pulley. The mechanical advantage of the pulley system increases as the number of movable wheels decreases. So if you have two wheels, you need twice as much force to lift the same weight because you need a movable pulley.
The mechanical advantage of a pulley system can be maximized by adding more pulleys or rope lengths. For example, if you have a single pulley system, the mechanical advantage is one of the smallest. By using two or three pulleys, up to five times the mechanical advantage can be achieved. You can also gain up to ten times the mechanical advantage by using multiple pulley systems.
The use of a single movable pulley system also adds to the mechanical advantage of the pulley system. In this case, you don't have to change the direction of the force to lift the weight. In contrast, a movable pulley system requires you to move the rope farther to generate the same force. Using a compound pulley system allows you to lift heavy loads with ease.
Safety Issues When Using Pulley Systems
Pulleys have an incredibly unique structure, consisting of a disc with a groove in the middle and a shaft running through it. A rope or cord is attached to one end of a pulley that turns when force is applied. The other end of the rope is attached to the load. This mechanical advantage means that it is much easier to pull an object using the pulley system than to lift the same object by hand.
Although pulley systems are a common part of many manufacturing processes, some employers do not train their workers to use them properly or install protection to prevent injury. It is important to wear proper PPE and follow standard laboratory safety practices during pulley system activities. Make sure any support structures are strong enough to handle the weight and weight of the rope or rope. If you do fall, be sure to contact your employer immediately.


editor by CX
2023-07-12
China Belt Conveyor Transmission Drive Pulley / Bend Pulley belt pulley
Item Description
Diverse Lagging Type:
Solution Features:
Conveyor Pulley is the main transmission belt conveyor components, there are two kinds of driveroller and the bend pulley, driving pulley may be made upon request, smooth or castrubber tread surface.
Complex Parameters: (The diameter can be made as needs.)
| Driving Pulley (rubber area) | |
| Belt Width | Normal Diameter of Pulley |
| five hundred mm | 500mm |
| 650 mm | 500mm,630 mm |
| 800 mm | 500mm,630mm,800mm,1000mm,1250mm,1400 mm |
| one thousand mm | 630mm,800mm,1000mm,1250mm,1400 mm |
| 1200 mm | 630mm,800mm,1000mm,1250mm,1400 mm |
| 1400 mm | 630mm,800mm,1000mm,1250mm,1400 mm |
| 1600 mm | 630mm,800mm,1000mm,1250mm,1400 mm |
| 1800 mm | 630mm,800mm,1000mm,1250mm,1400 mm |
| 2000 mm | 800mm,1000mm,1250mm,1400 mm |
| 2200 mm | 1000mm,1250mm,1400 mm |
| 2400 mm | 1000mm,1250mm,1400 mm |
| Bend Pulley (smooth surface & rubber surface) | |
| Belt Width | Regular Diameter of Pulley (mm) |
| five hundred mm | 250,315,four hundred,500 |
| 650 mm | 250,315,four hundred,500,630 |
| 800 mm | 250,315,400,five hundred,630,800,1000,1250 |
| a thousand mm | 250,315,400,500,630,800,one thousand,1250,1400 |
| 1200 mm | 250,315,400,500,630,800,a thousand,1250,1400 |
| 1400 mm | 315,four hundred,500,630,800,one thousand,1250,1400 |
| 1600 mm | four hundred,500,630,800,a thousand,1250,1400 |
| 1800 mm | four hundred,500,630,800,one thousand,1250,1400 |
| 2000 mm | five hundred,630,800,one thousand,1250,1400 |
| 2200 mm | 630,800,a thousand,1250,1400 |
| 2400 mm | 800,a thousand,1250,1400 |
Creation Processing
Our EPC Conveying Method Task in Mining, Coal, Energy Plant, Metallurgy, Metal Plant , Port & Wharf and other sector.
Company introduction
HangZhou Xihu (West Lake) Dis.ng Large Sector Machinery Co., Ltd is specialized in designing , building and production modern and systematic conveying machinery this sort of as belt conveyor, pipe conveyor, bucket elevator, screw conveyor, conveyor rollers, conveyor idlers, conveyor pulley, and a variety of types of components associated to the conveyors, which mainly utilized for mining, coal, metallurgy, power crops, dork, sea ports, grain, chemical, and other bulk material transmission industries.
HangZhou Xihu (West Lake) Dis.ng recognized because 2001 with whole registered capital of RMB 108 million, it addresses an spot of 80,000 square meters with construction spot of 26,000 square meters, present in excess of 400 specialized engineers and experienced workers. There are much more than 3 hundreds sets of specialized production equipments and testing machines to guarantee for the innovative technological innovation and large quality.
|
US $500-3,000 / Piece | |
1 Piece (Min. Order) |
###
| Certification: | ISO 9001, ISO14001, ISO8001, SGS, Ce |
|---|---|
| Pulley Sizes: | Type A |
| Manufacturing Process: | Casting |
| Material: | Carbon Steel |
| Surface Treatment: | Rubber Faced |
| Application: | Chemical Industry, Grain Transport, Mining Transport, Power Plant |
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
| Driving Pulley (rubber surface) | |
| Belt Width | Standard Diameter of Pulley |
| 500 mm | 500mm |
| 650 mm | 500mm,630 mm |
| 800 mm | 500mm,630mm,800mm,1000mm,1250mm,1400 mm |
| 1000 mm | 630mm,800mm,1000mm,1250mm,1400 mm |
| 1200 mm | 630mm,800mm,1000mm,1250mm,1400 mm |
| 1400 mm | 630mm,800mm,1000mm,1250mm,1400 mm |
| 1600 mm | 630mm,800mm,1000mm,1250mm,1400 mm |
| 1800 mm | 630mm,800mm,1000mm,1250mm,1400 mm |
| 2000 mm | 800mm,1000mm,1250mm,1400 mm |
| 2200 mm | 1000mm,1250mm,1400 mm |
| 2400 mm | 1000mm,1250mm,1400 mm |
###
| Bend Pulley (smooth surface & rubber surface) | |
| Belt Width | Standard Diameter of Pulley (mm) |
| 500 mm | 250,315,400,500 |
| 650 mm | 250,315,400,500,630 |
| 800 mm | 250,315,400,500,630,800,1000,1250 |
| 1000 mm | 250,315,400,500,630,800,1000,1250,1400 |
| 1200 mm | 250,315,400,500,630,800,1000,1250,1400 |
| 1400 mm | 315,400,500,630,800,1000,1250,1400 |
| 1600 mm | 400,500,630,800,1000,1250,1400 |
| 1800 mm | 400,500,630,800,1000,1250,1400 |
| 2000 mm | 500,630,800,1000,1250,1400 |
| 2200 mm | 630,800,1000,1250,1400 |
| 2400 mm | 800,1000,1250,1400 |
|
US $500-3,000 / Piece | |
1 Piece (Min. Order) |
###
| Certification: | ISO 9001, ISO14001, ISO8001, SGS, Ce |
|---|---|
| Pulley Sizes: | Type A |
| Manufacturing Process: | Casting |
| Material: | Carbon Steel |
| Surface Treatment: | Rubber Faced |
| Application: | Chemical Industry, Grain Transport, Mining Transport, Power Plant |
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
| Driving Pulley (rubber surface) | |
| Belt Width | Standard Diameter of Pulley |
| 500 mm | 500mm |
| 650 mm | 500mm,630 mm |
| 800 mm | 500mm,630mm,800mm,1000mm,1250mm,1400 mm |
| 1000 mm | 630mm,800mm,1000mm,1250mm,1400 mm |
| 1200 mm | 630mm,800mm,1000mm,1250mm,1400 mm |
| 1400 mm | 630mm,800mm,1000mm,1250mm,1400 mm |
| 1600 mm | 630mm,800mm,1000mm,1250mm,1400 mm |
| 1800 mm | 630mm,800mm,1000mm,1250mm,1400 mm |
| 2000 mm | 800mm,1000mm,1250mm,1400 mm |
| 2200 mm | 1000mm,1250mm,1400 mm |
| 2400 mm | 1000mm,1250mm,1400 mm |
###
| Bend Pulley (smooth surface & rubber surface) | |
| Belt Width | Standard Diameter of Pulley (mm) |
| 500 mm | 250,315,400,500 |
| 650 mm | 250,315,400,500,630 |
| 800 mm | 250,315,400,500,630,800,1000,1250 |
| 1000 mm | 250,315,400,500,630,800,1000,1250,1400 |
| 1200 mm | 250,315,400,500,630,800,1000,1250,1400 |
| 1400 mm | 315,400,500,630,800,1000,1250,1400 |
| 1600 mm | 400,500,630,800,1000,1250,1400 |
| 1800 mm | 400,500,630,800,1000,1250,1400 |
| 2000 mm | 500,630,800,1000,1250,1400 |
| 2200 mm | 630,800,1000,1250,1400 |
| 2400 mm | 800,1000,1250,1400 |
How to Assemble a Pulley System
A pulley is a wheel that rotates on a shaft or shaft to support the movement of a taut cable. Pulleys allow power to be transmitted from the shaft to the cable.
Simple pulley
The simplest theory of operation of a pulley system assumes that the rope and weight are weightless and that the rope and pulley are not stretched. Since the force on the pulley is the same, the force on the pulley shaft must also be zero. Therefore, the force exerted on the pulley shaft is also distributed evenly between the two wires passing through the pulley. The force distribution is shown in Figure 1.
The use of simple pulleys is as old as history. Before the Industrial Revolution, people relied on muscle strength to carry heavy loads. Pulleys, levers and ramps make this possible. Today, we can see pulleys in a variety of systems, from exercise equipment to garage doors, and even rock climbers use them to help them reach greater heights. As you can see, these simple machines have been around for centuries and are used in everyday life.
Another simple pulley system is the pulley system. In this system, there is a fixed pulley at the top and a movable pulley at the bottom. The two pulleys are connected by a rope. This combination reduces the amount of work required to lift the load. Additionally, the ropes used in this system are usually made of rope and woven through the individual wheels of the pulley drum.
A pulley is an ingenious device that distributes weight evenly and can be used to lift heavy objects. It is easy to build and can be easily modified for a wide range of activities. Even young children can make their own with very few materials. You can also use simple household items such as washing machines, thin textbooks and even chopsticks. It's very useful and can be a great addition to your child's science and engineering activities.
The simplest pulley system is movable. The axis of the movable pulley can move freely in space. The load is attached to one end of the pulley and the other end to the stationary object. By applying force on the other end of the rope, the load is lifted. The force at the other end of the rope is equal to the force at the free end of the pulley.
Another form of pulley is the compound pulley. Compound pulleys use two or more wheels to transmit force. Compound pulleys have two or more wheels and can lift heavier objects. Dim is POLE2.
tapered pulley
It is important to clean and align the bolt holes before assembling the tapered pulley. The screws should be lubricated and the threads cleaned before installation. To install the pulley, insert it into the shaft keyway. The keyway should be aligned with the shaft hole to prevent foreign matter from entering the pulley. Then, alternately tighten the bolts until the pulley is tightened to the desired torque.
A tapered pulley is a basic structure. The pulley belt is arranged across four steps. Installed between the headstock casting and the main shaft, it is often used in the paper industry. It integrates with printing machinery and supports assembly lines. These pulleys are also available in metric range options, eliminating the need for ke-waying or re-drilling. They are easy to install, and users can even customize them to suit their needs.
CZPT Private Limited is a company that provides unique products for various industries. This large product is used for many different purposes. Also, it is manufactured for industrial use. The company's website provides detailed specifications for the product. If you need a tapered pulley, contact a company in your area today to purchase a quality product!
Tapered pulleys are vital to paper mill machinery. Its special design and construction enable it to transmit power from the engine source to the drive components. The advantages of this pulley include low maintenance costs and high mechanical strength. Cone wheel diameters range from 10 inches to 74 inches. These pulleys are commonly used in paper mills as they offer low maintenance, high mechanical strength and low wear.
A tapered sleeve connects the pulley to the shaft and forms an interference fit connector. The taper sleeve is fixed on the shaft with a key, and the corresponding inner hole is fixed on the shaft with a key. These features transmit torque and force to the pulley through friction. This allows the tapered pulley to move in a circular motion. The torque transfer characteristics of this pulley are most effective in high speed applications.
The sleeve is the most important part when assembling the tapered pulley. There is an 8-degree taper inside the cone, which is closely connected to the inner surface of the pulley. Taper sleeves and pulleys are interchangeable. However, tapered pulleys can be damaged after prolonged use.
pulley pulley system
A pulley pulley system is a great way to move heavy objects. These systems have been around for centuries, dating back to the ancient Greeks. This simple mechanism enables a person to lift heavy objects. These blocks are usually made of rope, and the number of turns varies for different types of rope. Some blocks have more cords than others, which creates friction and interferes with the easy movement of the lifting system.
When using a pulley pulley, the first thing to decide is which direction to pull. Unfavorable rigging means pulling in the opposite direction. In theory, this method is less efficient, but sometimes requires a certain amount of work space. The benefit is that you will increase the mechanical advantage of the pulley by pulling in the opposite direction. So the interception and tackle system will give you more of a mechanical advantage.
Pulley pulleys are an excellent choice for lifting heavy objects. The system is simple to install and users can easily lift objects without extensive training. Figure 3.40 shows a pulley in action. In this photo, the person on the left is pulling a rope and tying the end of the rope to a weight. When the rope is attached to the load, the rope will be pulled over the pulley and pulley.
The blocks on the blocks are attached to the ends of the rope. This creates unique lifting advantages compared to single-line systems. In Figure 3, the tension of each thread is equal to one-third of the unit weight. When the rope is pulled over the pulley, the force is divided equally between the two wires. The other pulley reverses the direction of the force, but that doesn't add any advantage.
Use pulleys to reduce traction and load. The weight of the load has not changed, but the length of the rope has increased. Using this method, lifting the load by pulling the rope four times reduces the force required to lift one foot. Likewise, if the pulley system had four pulleys instead of three, the length of the rope would be tripled.
The system can transmit loads in any direction. Rope length is determined by multiplying the distance from the fixed block to the load by the mechanical advantage. If the mechanical advantage is 3:1, then passing the rope through the pulley 3 times will produce the required traction distance. Also, the length of the rope will depend on the mechanical advantage, so if the load is three times the length of the rope, it will be more than three times the required length.


editor by czh 2023-01-04
China Professional Belt Tension Pulley Yes Timing Belt and Pulley Drive Compressor Belt Tension Pulley 5mm Pitch Timing Pulley wholesaler
Product Description
Product Description
|
Product Name |
belt tensioner pulley |
|
OEM No. |
Standard |
|
MOQ |
10PCS |
|
Package |
Neutral box,Customized box |
|
Quality |
Good quality |
|
Shipping Port |
Usually in HangZhou Port. The port specified by the customer is acceptable. |
|
Sample |
Available |
|
Shipment |
By sea or by express(DHL,TNT,Fedex and EMS etc.) |
|
Warranty |
1 year |
|
STOCK |
5000 PCS |
Certifications
Packaging & Shipping
Company Profile
HangZhou HangZhou Auto Parts Co., Ltd. was established in 1999, located in HangZhou, ZHangZhoug, with beautiful scenery and convenient transportation! The company was formerly known as HangZhoung, HangZhou, and officially changed its name to HangZhou. The company covers the whole car parts with cooling system, steering chassis system, suspension system, braking system, ignition system, fasteners,etc. In-depth cooperation with many large domestic factories, our products are exported to home and abroad! Whether you choose the current product from the catalog or customize it for you, we can meet your needs! We have a pursuit of CZPT in product quality!
Twenty years of industry refining, we have learned too much. We abide by the integrity of business, serve with heart, always take customer satisfaction as the axis, think, take action, create real value for customers, exchange heart with customers, go hand in hand Win-win situation!
Our philosophy and purpose are: based on integrity, sincere service, the pursuit of excellence, return to society, think and realize, realize and act, and go high!
Our Advantages
FAQ
Q1. How many years does your company trade in auto parts?
A: We have been established for More than 20 years.
Q2. Where is your company?
A: We are located in ZHangZhoug
Q3. What is the delivery date?
A: If it takes 5~7 days for inventory, it will take 20-40 days if there is no inventory.
Q4. What is a package?
A: Neutral packaging or customer packaging.
Q5. What is the payment method?
A: Our payment method: T / T
Q6. What is the payment terms?
A: Our payment terms: After full payment
Q7. How is the quality?
A: Strict control before shipment.
Q8. What is a guarantor?
A: 12 months.
Q9. Can you help with the delivery of the goods?
A: Yes. We can help deliver goods through our customer freight forwarders or our freight forwarders.
Q10. Can you provide samples for free?
A: It depends on the cost of the sample, but we do not pay the shipping cost.
Q11. Which port does our company supply?
A: Usually in HangZhou Port. The port specified by the customer is acceptable.
Why You Should Get a New Timing Belt
A timing belt is a rubber belt with teeth that transfer rotary motion from the central motor to the drive pulley. It prevents the piston from striking the valves at a critical level. Unfortunately, these belts cost a lot to replace. Here are some reasons why you should consider getting a new one. If you're not sure whether a new timing belt is necessary, read on. You can also save money by avoiding unnecessary repairs and replacements by choosing an aftermarket timing belt.
Timing belts are rubber belts with hard teeth
While it's true that timing belts are commonly known as "drive belts," there are several different types of belts that are used in engines. Despite their commonity, timing belts are made of different materials. The material used to make them is important because it can either negatively impact performance or negatively affect its life span. Whether it's a car, truck, or motorcycle, timing belts are an essential part of your engine.
Among their many advantages, timing and drive belts are designed to reduce friction, increase speed, and transmit torque more efficiently. In fact, the design of timing belts is similar to that of a cam belt. Both belts work in conjunction with each other to increase the torque and speed of a vehicle. In both types, the teeth of the belt are aligned at the same angle. In a small-scale drive system, this elongation is minimal, but if the load is too high, the teeth of the belt will begin to jump or cog over the pulley's teeth, causing the noise.
Timing belts are used to synchronize the movement of the crankshaft and camshaft. Timing belts have hard teeth on the inner side of the belt and interlock with the cogwheels on the crankshaft and camshafts. Because of this, they make it easier for the exhaust and intake valves to open and close at the proper time. Timing belts are made of high-10sile rubber, but they may also be polyurethane, welded urethane, or moulded polyurethane.
When a timing belt is worn, it may degrade. The teeth will gradually lose their shape over time and the belt will begin to slip. If the teeth become rounded, the belt may still work, but its timing will be off. Hence, it is vital to replace the timing belt if you notice these signs. If you find any damage, contact a qualified mechanic for repair. If the teeth are worn or damaged, consider replacing the entire belt.
When it comes to a car's engine, timing is vital. Timing belts connect the internal moving parts of the engine. In addition to timing, they can also power water, oil, and injection pumps. And it's vital to make sure your timing belt doesn't get damaged because it will not function properly. So don't neglect timing belts unless you're certain they're damaged.
They transfer rotary motion from the central motor to the drive pulley
A timing belt is a mechanical device that transfers rotary motion from a central motor to a drive pulley through a chain. The belt must be wide enough to accommodate the torque that will be produced by the design. The belt must be wider than the size selected for the drive pulley. In order to determine the correct belt width, the center-to-center distance between the drive pulley and the central motor is measured.
Unlike the elastic belt, which tends to stretch when pressed against a large load, the timing belt does not suffer from this problem. Instead, it exhibits low torsional stiffness, which allows it to transfer rotary motion efficiently. The timing belt also reduces the likelihood of slippage. This is because the cord material is very strong compared to the loads that it must handle.
The most common type of timing belt pulley is made of nylon. The advantage of nylon is that it has a natural lubrication surface and is relatively low-maintenance. It is also durable, malleable, and low-melting point. It is also highly resistant to wear and tear and is suitable for applications that are exposed to high temperatures. However, the belt must be cleaned and maintained on a regular basis.
A Timing belt can be used in a variety of applications. For instance, the timing belt is used in automotive engines. However, the timing belt is also found in stationary power generators, marine engines, and aviation engines. Additionally, it is used in conveyors, winches, treadmills, and washing machines. It also plays a crucial role in the curtain at a theater hall.
The timing belt can be flat, V-shaped, or trapezoidal. The latter is usually made of rubber. The distance between the 2 pulleys is between 5 and 10 meters. The flat belts transmit power through friction between the belt and the pulley. The efficiency of flat belts is approximately 98% and it makes very little noise. However, it must be used in conjunction with the appropriate motor drive. Ultimately, the engineers must choose the best 1 that can deliver the torque that the drive pulley needs to generate.
They prevent pistons from striking the valves on a critical level
In an interference engine, the valves and pistons share the same space in the cylinder, but they move at different rates. While 1 or more of the valves may open into the piston's travel area, the other is closed and never makes contact with the piston. Timing belts prevent this critical collision from occurring and prevent the piston from damaging the engine. Most timing belts fail at start-up and shutdown. Check the car owner's manual for recommended replacement intervals.
The timing belt synchronizes the rotation of the crankshaft and camshaft. The timing belt allows the piston to move without striking the valves, allowing the engine to perform its essential functions. The camshaft is used to push fuel and air into the cylinder. The valves close and open as the engine moves forward. When the engine is running, the timing belt prevents the piston from striking the valves on a critical level.
Because of their critical role in the engine, timing belts are often an overlooked component. Without proper timing, an engine will not work properly, and valve damage can be costly. If timing fails, the piston will strike the valves on a critical level, which will damage the engine. Timing belts are a vital automotive component, so make sure yours is in good condition.
A timing belt is a necessary part of your Subaru's engine. It synchronizes the crankshaft and camshaft to prevent problems with the engine. If a timing belt breaks, the pistons will strike the open valves and cause massive engine damage. Timing belts must be replaced when recommended in your owner's manual. If it breaks, the engine will shut down.
They cost a lot to replace
Timing belts are expensive to replace, with the average car owner paying $1,200 to have them replaced. Most cars have transverse engines, where the cam cover rests against the driver's side of the engine. These specialty cars are notoriously difficult to service and require the services of a specialist mechanic. Timing belts are a complex system with a series of idler bearings and tensioner bushes to guide and drive the belt. These components are often replaced at the same time as other routine maintenance work, and they may cost you a bundle.
If you have a car that's been in the shop for a while, timing belt replacement may be the only option. A timing belt that's popped isn't going to make the car run, so you'll need to get it replaced. If you need the belt replaced, you can use a car service, or you can try to replace the timing belt yourself. It's a good idea to get several quotes before making the decision to replace the belt.
Depending on the make and model of your car, timing belt replacement costs may range from $250 to more than $1,000. Prices will vary according to vehicle type, labor hours, and the brand of parts and labor. If you don't have a mechanic handy, you can always use a free online tool like CZPT to get an estimate for timing belt replacement and find a mechanic near you. This will help you save money and avoid the hassle of spending a lot of money on an unnecessary repair.
While timing belts typically last between 60,000 and 100 thousand miles, you may only need to replace them once in your car's lifetime. Timing belts may seem cheap at first, but if you're planning on selling your car, you'll want to avoid the expense of replacing your timing belt. If you don't, your car's engine may run poorly and cause your car to use more fuel than it should.


China factory Auto Drive Belt Tensioner OEM 11288604266 Alternator Pulley for BMW near me factory
Product Description
Auto Drive Belt Tensioner OEM Alternator Pulley For BMW
Product Specification:
| OEM | 11288604266 |
| Apply To |
For car |
| Brand | FENGMING |
| Condition | Brand New |
| Stock Availability | Yes |
| Minimum Order QTY | 2PCS |
| OEM Order Acceptability | Yes |
| Small order Lead Time | 3-7 days |
| Large Order Lead Time | 15-30 days |
| Quality Warranty | 12 months |
| PACKAGING | As neutral or as customer's request, FENG MING PACKING |
| Payment Methods | Paypal, Western Union, Bank T/T, L/C |
| Shipment Methods | DHL, UPS, TNT, FedEx, Aramex, EMS, Air Cargo, Sea Cargo |
Company Profile
Tips For Replacing a Belt Tensioner
When replacing a serpentine belt or automatic tensioner, you will need a special tool. This tool has a long, flat extension handle that allows you to place a socket onto the bolt and flats on the tensioner arm. The following are some tips to follow when replacing the belt or tensioner on your vehicle. To replace your belt or tensioner, you should start by checking the tensioner's lubrication.
Serpentine belt
If you notice that the power steering or air conditioning are not working, you should check the serpentine belt tensioner. A malfunctioning serpentine belt tensioner can lead to a host of other issues. The belt may stretch, which can be caused by several factors. Over time, serpentine belt tensioners can also get worn down. Additionally, they can have a variety of other problems, including rust or dirt in the housing.
You can replace your serpentine belt by following the instructions found on your vehicle's manual. Some tensioners attach to the engine via a single bolt. To remove and replace the belt, remove the old unit and the retaining bolt. Locate the locking pin in the engine and place the new tensioner over it. Use a torque wrench or hand tool to tighten the bolts. When installing the new tensioner, be sure to line up the mounting bolt holes with the mounting bolts. Once the tensioner is installed, test the tension by ensuring that the gauge is above the ribs. If it slides down, it is time to replace the tensioner.
Before you begin the process of replacing your serpentine belt, be sure to park your vehicle in a level area. Turn off the engine and chock both rear wheels before starting the process. Using a diagram from your vehicle's repair manual can make the process easier, especially if you are a beginner. You can draw it in your hand, or refer to a repair manual to find out the exact location of the tensioner pulley.
If you notice that the belt is slipping or squealing while driving, it may be time to replace the serpentine belt tensioner. A worn-out belt can cause the belt to slip and can cause power steering, air conditioning, and alternator malfunctions. You should also check the belt tensioner regularly. The motor may stall or make a loud noise. These are all signs of worn-out serpentine belt.
A serpentine belt uses less space in the engine than a V-belt. It also provides more tension for the serpentine belt, which prevents it from running hot and squealing. Serpentine belts are manufactured to last for several hundred thousand miles. They are a must-have item for your car! So be sure to keep it maintained and properly adjusted! Then, you can be sure to have your car running smoothly and safely.
If you notice any of these symptoms, you should replace your serpentine belt tensioner. A serpentine belt tensioner is a simple self-10sioning device that is mounted on the front of the engine. These devices are usually easy to replace and are not complicated to install. You can find 1 at any parts store or online. When the time comes to replace your serpentine belt, don't hesitate to get the parts you need from a local auto part store.
Idler pulley
The idler pulley and the belt tensioner are essential components of your car's drivetrain. If any 1 of them fails, all of them must be replaced. This is because they were manufactured at the same time and most likely have the same number of miles on them. As a result, they can all fail within a few thousand miles of each other. Here are some of the symptoms that you should look for when inspecting your idler pulley or belt tensioner.
Idler pulleys are a common part of most cars. They play a vital role in the operation of the belt system by directing the belt's path and providing additional contact with the pulley. The idler pulley is also responsible for turning the cooling fan in an air-cooled Corvair engine. Because of these functions, idler pulleys are often replaced with idlers that differ in size.
Idler pulleys are small, 2 to 4 inches in diameter and mounted on the front of the engine block. Their purpose is to create a constant amount of tension on the drive belt. When the idler pulley is worn out, the accessory drive belt may experience excessive vibration and squealing noises. You may wish to replace it as soon as possible. You can do so at AutoZone.
A worn or damaged idler pulley will require a replacement. The belt itself will not fall off the car unless the idler pulley is damaged. A squealing sound can be a sign of a broken spring. Alternatively, a mechanic can recommend a replacement based on the condition of the idler pulley. In most cases, idler pulleys are more durable than the belts and are therefore recommended for replacement.
You can also notice that the idler pulley is slipping or causing excessive noise. Its constant rotation wears the idler pulley and reduces the tension of the belt. This causes the belt to slip and may even tear off the engine. Ultimately, this could result in stalling. And if you notice the engine belt squealing or making excessive noises, you should consider replacing it.
An idler pulley for a belt tensioner are often confused. Though both of them are used in the same application, they differ in many ways. The tensioner is the 1 that receives pressure from the belts and moves them. The idler pulley is not attached to an adjustable bolt, and it can cause unusual noises. It might even make squealing or odd noises.
Spring tensioner
A spring belt tensioner is a solution to a loose belt. It features a strong torsion spring that reduces slack. These devices are designed to fit up to 6mm wide belts. They are highly reliable and durable. They are also suitable for applications where the engine speed is often fluctuating. Here's how you can choose the best 1 for your vehicle. The spring in the tensioner should be in the proper position to keep the belt taut and free of slippage.
The RunRight tensioner is a durable, high-quality product that uses aluminum alloy. Its elastomeric inserts rely on highly elastic natural rubber for good shape memory and durability. Spring tensioners are easy to install and maintain. They are designed for both axial and helical drives. They feature detailed technical drawings and 3-D models to help you determine the best 1 for your application. To choose a spring tensioner, visit our website.
A worn bushing in the tensioner pulley or a loose pivot arm can result in excessive noise, vibration, and premature belt failure. In addition, worn springs cannot maintain proper tension. Over time, they lose tension. The pulley arm itself can also become damaged, preventing it from rotating properly. If these problems occur, you'll need to replace the spring tensioner. If you don't see any signs of wear, check your mounting bracket and tensioner.
A worn pivot bushing can cause the tensioner arm to misalign, leading to excessive back and forth sway. It may also cause the tensioner to jam, which means the belt is too long or too short. If you notice excessive wobble, you should replace the spring tensioner. A faulty tensioner may also be causing excessive oscillation in the pulley. To determine if the spring tensioner is too weak or jammed, check the belt's length by using a breaker bar or socket with a long handle ratchet.
When it's time to replace your serpentine belt, don't forget to replace the belt tensioner. The tensioner protects other components from premature failure. It is a relatively inexpensive repair. It should be replaced as part of a larger multi-ribbed belt. It also provides protection for other components of the drive system. In addition to its protection and performance, the tensioner is inexpensive and relatively easy to replace.
It's vital to check the tensioner and idler pulleys to make sure the system is aligned properly. If they don't align, the belt will slip and cause premature wear. Alternatively, the tensioner may have too much tension, overloading the shaft bearings and causing premature failure in other parts. You should also check the idler pulleys for noise as well, since these are engine-driven accessories.


China factory Low Price Auto Parts Car Accessories Belt Drive V-ribbed Belt Tensioner Pulley OEM 1175000QAH 7700868201 7700870795 for Nissan Kubistar Box 1.2L near me factory
Product Description
Product Description
Low Price Auto Parts Car Accessories Belt Drive V-ribbed Belt Tensioner Pulley OEM 1175000QAH 77 for Nissan Kubistar Box 1.2L
Water Pump for DACIA
Water Pump for NISSAN
Water Pump for RENAULT
All kinds of car water pumps can be produced for you. Welcome to your inquiry.
| MIC NO. | REF&OEM NO | APPLICATION | YEAR | PHOTO |
| TB34RE9601 | 951154 77 8201 8200040155 |
DACIA LOGAN (LS_) 1.2 16V DACIA SANDERO 1.2 16V DACIA SANDERO 1.2 16V LPG DACIA SANDERO II 1.2 NISSAN KUBISTAR Box (X76) 1.2 NISSAN KUBISTAR Box (X76) 1.2 16V RENAULT CLIO II (BB_, CB_) 1.2 (BB0A, BB0F,, BB2H, CB0A,... RENAULT CLIO II (BB_, CB_) 1.2 16V (BB05, BB0W, BB11BB2V, CB05,... RENAULT CLIO II (BB_, CB_) 1.2 LPG RENAULT CLIO II (BB_, CB_) 1.2 LPG (BB0A, CB0A) RENAULT CLIO II Box (SB0/1/2_) 1.2 (SB0A, SB0F, SB10) RENAULT CLIO II Box (SB0/1/2_) 1.2 (SB0A, SB0F, SB1K, SB2D) RENAULT KANGOO (KC0/1_) 1.2 (KC0A, KC0K, KC0F, KC01) RENAULT KANGOO (KC0/1_) 1.2 16V (KC05,KC06,KC03,KC0T,KC0W,KC1D) RENAULT KANGOO Express (FC0/1_) 1.2 (FC01, FC0A, FC0F) RENAULT KANGOO Express (FC0/1_) 1.2 (FC1A) RENAULT KANGOO Express (FC0/1_) 1.2 16V (FC05, FC1P, FC1K, FC0T) RENAULT THALIA I (LB_) 1.2 16V RENAULT TWINGO I (C06_) 1.2 (C066, C068) RENAULT TWINGO I (C06_) 1.2 (C067) RENAULT TWINGO I (C06_) 1.2 16V (C060) RENAULT TWINGO I (C06_) 1.2 16V (C06C, C06D, C06K) |
2006- 2008- 2008- 2012- 2003- 2006- 1998- 2001- 1998-2009 1999-2001 1999-2003 1998- 1997- 2001- 1997- 1998-2001 2001- 2002- 1996-2007 1996-2007 2004-2007 2001-2007 |
Company Profile
Our Factory
Exhibition Shows
FAQ
Q1: Are you a trading company or manufacturer?
A1: We are industrial and export combination.
Q2: If there's any quality problem, what would you do to guarantee our rights?
Q2: We seldom get complains from our customers so far. If it really happens, we'll be responsible for that.
Q3: How long is your delivery time?
Q3: Around 30-45 days if no stock; Around 7 days when stock available.
Q4: What's your sample policy?
A4: Samples under $50.0 will be no charge, however the freight charge should be borne on buyer's account.
Normal delivery time will be 4 days when stock available.
Replacing a Failing Drive Belt Tensioner
A failing drive belt tensioner can be extremely costly. Here's what to look for and what to do if you suspect yours is bad. In addition, you'll learn how to identify Idler pulleys and repair it yourself. If the tensioner is failing, you should replace the belt, as well as the Idler pulleys and shaft bearings. But what if the tensioner isn't faulty?
Symptoms of a bad or failing drive belt tensioner
If your car's drive belt is not moving smoothly, the pulley may be at fault. Ideally, the tensioner pulley should move away from the engine when the car starts. However, if it stays put or starts to move toward the engine, it's time to replace the tensioner. The belt may also start to exhibit different wear patterns, such as the uneven wear of the sprockets, bearings, and springs.
If the serpentine belt begins to look loose and the engine loses its luster, the problem is most likely the bad drive belt tensioner. This issue will result in engine vibration. A faulty drive belt tensioner may also lead to a faulty spark plug, which prevents fuel from burning in the combustion chamber. This issue will likely require an engine diagnostic tool, such as an OBD2 scanner, to determine the cause of the check engine light.
Another sign that your drive belt tensioner is failing is a chirping noise. This noise can occur intermittently or constantly, and it may signal a problem with the pulley. In some cases, a faulty pulley may even cause your engine to misfire. Additionally, you may notice that the engine won't start, even if you engage the starter motor.
In addition to the noise that may come from a failing tensioner, the bad belt tensioner may cause your serpentine to fail. In addition to the noise, this can also lead to overheating of the engine, which can result in costly damages. In addition to causing engine damage, a bad belt tensioner won't reserve the minimum tension it needs to do its job and may even exceed it, causing the belt to wear out much faster.
If you notice any of these symptoms, it may be time to replace the drive belt tensioner. You can find a replacement OEM part online at a discounted price, as they're available in wholesale quantities. A Mazda engine typically has no other parts blocking the serpentine belt path, so you can easily find the part you need. After replacing the drive belt tensioner, you'll need to replace the serpentine belt as well.
Cost to replace a drive belt tensioner
Depending on the location and type of vehicle, replacing a drive belt tensioner can cost between $235 and $267. Some repairs may require other parts, such as a serpentine belt or tensioner housing. RepairPal's Fair Price Estimator can help you get an accurate estimate for your particular vehicle. You can also contact HomeX, a virtual repair shop that can fix simple issues like loose drive belt tension.
It's a relatively simple DIY job for most cars. An experienced mechanic will be able to replace the belt in a half hour or less, depending on the type of car and how many parts are affected. Depending on the complexity of the repair, the labor to replace the drive belt tensioner could cost anywhere from $50 to $170. The labor to replace the drive belt tensioner is typically included in the quoted price, but some auto shops may charge more to replace other car parts as well.
Replacing the drive belt tensioner is a relatively easy task. While the process might take an hour or more, it will be worthwhile in the long run. Regular inspections can prevent costly repairs by identifying problems before they cause major damage. A car's belt is essential to the operation of the engine and can't be operated without it. Changing it can save you money, as it will save you from spending extra on unnecessary parts.
Thankfully, there are plenty of tools available to help you replace your drive belt. While it may not be the easiest repair, it will still cost less than a mechanic's service call. It is better to replace the belt early than to wait for the vehicle to break down, as this will prevent more expensive parts from breaking. You may also consider investing in a premium belt, which will give you twice as much mileage as a cheaper one.
While a drive belt tensioner is generally considered a wear-and-tear item, it is a part that should last the entire life of the vehicle. You can expect to replace the drive belt tensioner no earlier than 125,000 miles, but it is better to do it early if your car isn't that old. And it doesn't hurt to check the owner's manual for directions on how to replace the drive belt tensioner.
Idler pulleys
Idler pulleys may seem like a minor part of your car, but their important job is to keep various components in good working order. Fortunately, they are inexpensive and don't need much maintenance. If 1 pulley fails, it is best to replace all of them. However, it is not always easy to check idler pulleys yourself. It's recommended that you visit a professional auto repair shop that is ASE-certified to inspect and replace the idler pulley.
Depending on the size and type of idler pulleys you need, you'll have to purchase 2 or 3 pieces. You'll need to purchase a pair of pliers for this part, as well as a tensioner pulley wrench. The cost of a replacement idler pulley will vary by make and model, but you can expect to pay between $40 and $200. These prices don't include taxes or fees. Because they are so essential to drive belts, it's worth investing in 1 or two.
Idler pulleys are a vital part of a car's engine. They're found underneath the hood and are usually 2 to 4 inches in diameter. They run over a roller that's used to tension the belt. The belt is wrapped around a series of engine parts, and the idler pulleys are a complement to each other. You may not need an idler pulley on your car, but your mechanic will install it for you if you don't.
The idler pulleys for a belt tensioner are crucial parts of your car's engine. If they are worn down, the belt is likely to move loosely over them. Corrosion may also make the idler pulley move less freely. If the idler pulley is slipping, the belt may jump over the pulley, and the squealing noises will indicate a serious problem.
The idler pulley is a pivotal part of the engine's power train. It redirects the path of the serpentine and timing belts, so that they can make optimal contact. The larger the contact patch, the more power the belt will transfer. The idler pulley can also improve the vehicle's performance. It is a vital part of the engine, so make sure you check it frequently and install it correctly.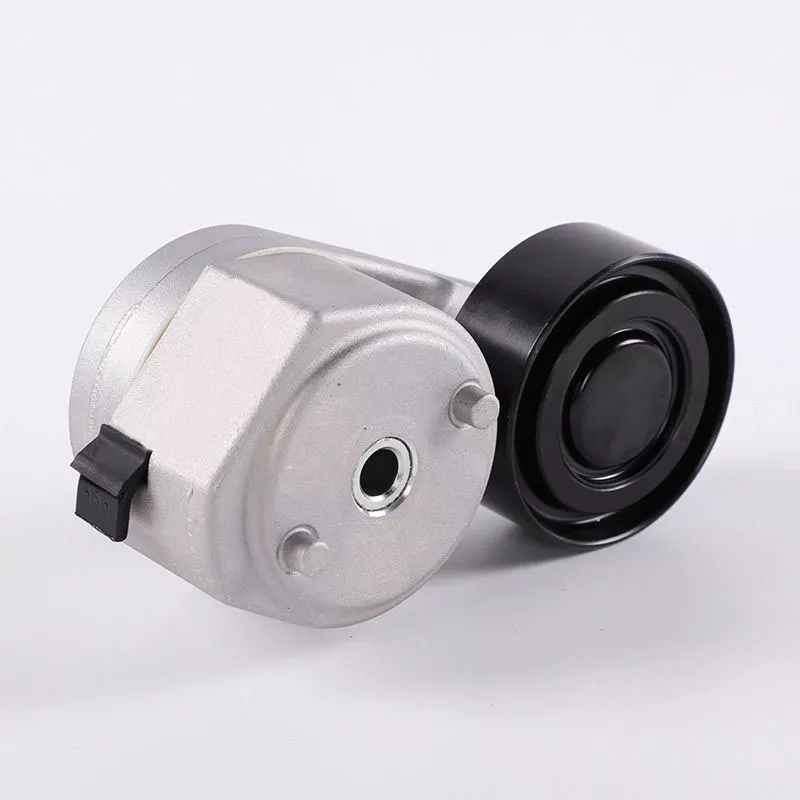
Repairing a drive belt tensioner
Replacing a drive belt tensioner is relatively simple. While your belt may need to be replaced, other parts of your engine may also need to be fixed. Typically, the tensioner will be replaced along with the pulley, as both parts are prone to malfunction. Replacing the drive belt tensioner is a fairly straightforward job, and it should only take about an hour or two. By following these simple steps, you can save yourself a lot of money and time.
You can detect the problem by observing the belt glazing. Typically, it occurs when the tensioner does not have enough spring tension. Another sign of a failed component bearing is excessive arm oscillation. Excessive chattering and oscillation indicate that the damper has worn out. If you notice excessive oscillation, you should replace the tensioner pulley. Otherwise, you might be dealing with a defective bearing.
A damaged or out-of-adjusted drive belt will make a squealing noise. This is due to the belt slipping on the pulleys. It is most noticeable when the car is first started in the morning. A damaged drive belt will also be hard to manipulate. The new belt should be the same length and width as the old one. You can check the tensioner by pulling the belt and compressing it.
A worn-out drive belt tensioner will result in unusual noise, excessive wear, and a loose belt. This is especially affecting if the car is equipped with a serpentine belt. The drive belt tensioner has a roller bearing that can wear out, which will cause a squealing noise or even cause the belt to roll off entirely. Because of its important role in engine operation, it is vital to check the condition of the drive belt tensioner on a regular basis.
While replacing a drive belt tensioner may seem like a simple DIY project, you should consult a mechanic before undertaking the work. The parts and labor costs of a drive belt tensioner repair can range from $140 to $400, and you should allow an hour for this repair. If you are not comfortable performing the repair yourself, you can always hire a mechanic to do it for you. In most cases, a drive belt tensioner replacement will cost approximately $70 to $80 and take about an hour.

